Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
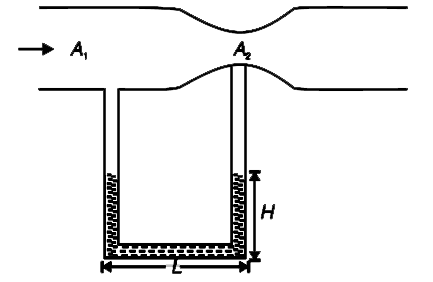
- A horizontal tube having cross sectional area A(1)=10cm^(2) has a vent...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal tube has different cross sections at points A and B. The ...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid flows through a horizontal tube. The velocities of the liquid...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid flows through a horizontal tube as shown in figure. The veloc...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal tube having cross sectional area A(1)=10cm^(2) has a vent...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Air (density=rho) flows through a horizontal venturi tube that dis...
Text Solution
|
- A portion of a tube is shown in the figure. Fluid is flowing from cros...
Text Solution
|
- From a horizontal tube with area of cross-section A(1) and A(2) as sho...
Text Solution
|
- If cross- sectional area of limb I is A(1) and that of limb II is A(2)...
Text Solution
|