Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
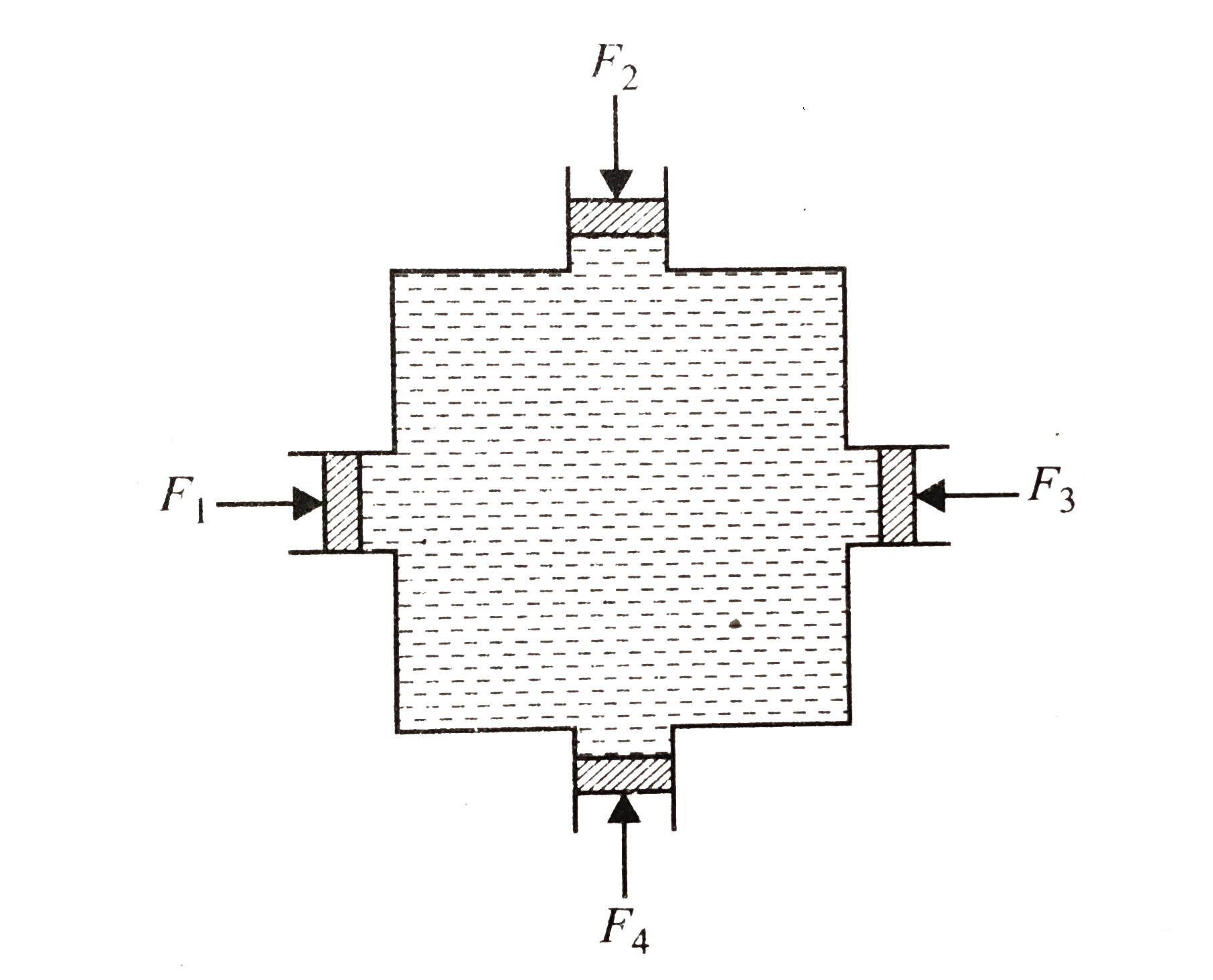
- Figure shows water filled in a symmetrical container. Four pistons of ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows water filled in a symmetrical container. Four pistons of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two syringes of different cross-section (without needle filled with wa...
Text Solution
|
- Initial volume of H(2) gas saturated with water vapour is confined und...
Text Solution
|
- A cylindrical adiabatic container of total volume 2V(0) divided into t...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder fitted with movable piston contains liquid water in equilib...
Text Solution
|
- Two syringes of different cross-section (without needle filled with wa...
Text Solution
|
- जल से भरी हुई भिन्न अनुप्रस्थ परिच्छेद (बिना निडिल वाला) की दो पिचकारी...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows water filled in a symmetrical container. Four pistons of ...
Text Solution
|