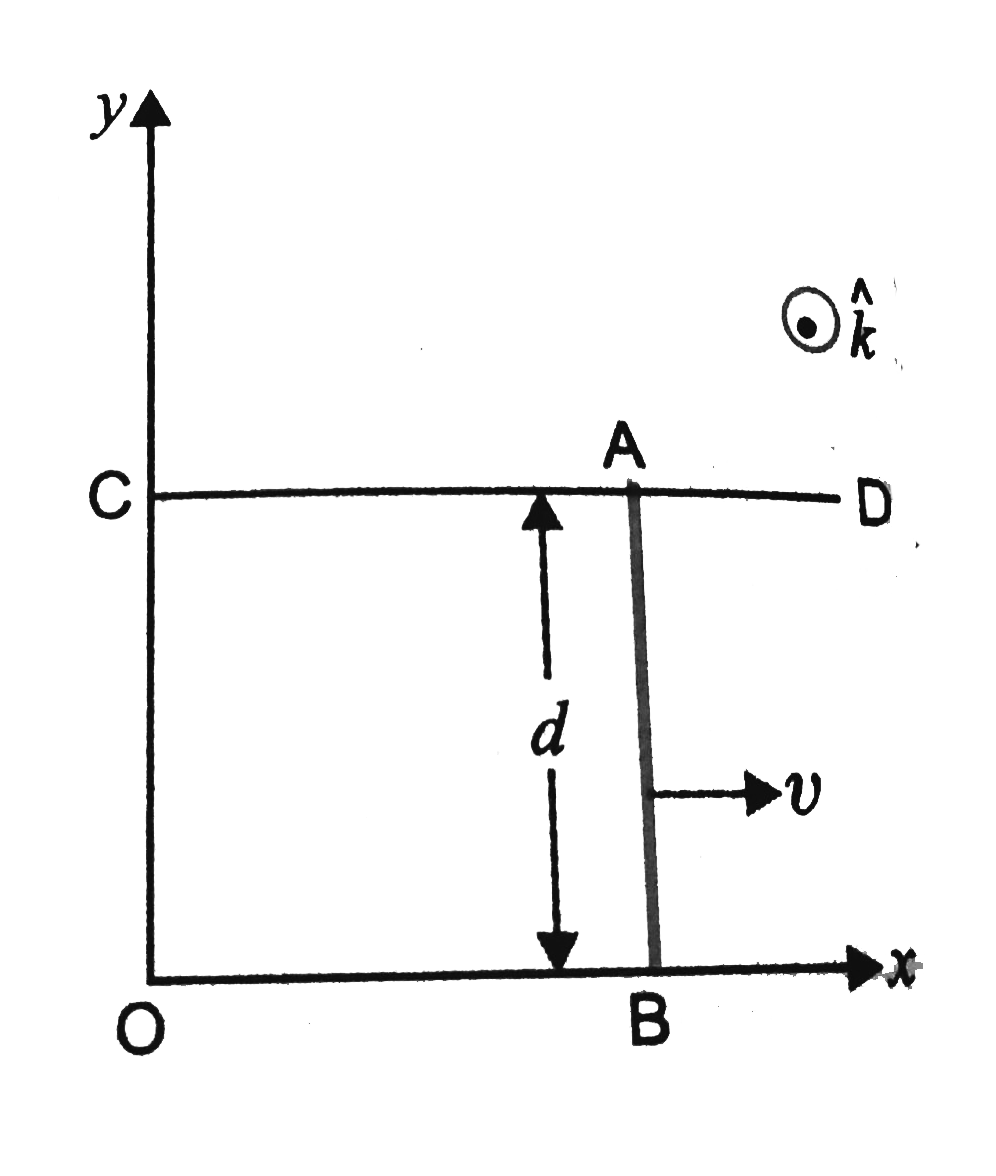
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A magnetic field B = B(0) sin (omega t) hat k covers a large region wh...
Text Solution
|
- Find the current in the wire PQ for the configuration shown in Fig. Wi...
Text Solution
|
- A magnetic field B = B(0) sin (omega t) hat k covers a large region wh...
Text Solution
|
- Find the current in the sliding rod AB (resistance = R) for the arrang...
Text Solution
|
- Two infinite parallel wire, having the cross sectional area 'a' and re...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting wire XY of mass M and negligible resistance slides smothl...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform magnetic field vec(B) = B(0) hat(k) exists in a region. A cu...
Text Solution
|
- In the below circuit , AB is a wire of length 100 cm with 5Omega resis...
Text Solution
|
- दो लम्बी समान्तर धातु की तारें एक प्रतिरोध R के साथ क्षैतिज त...
Text Solution
|