Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
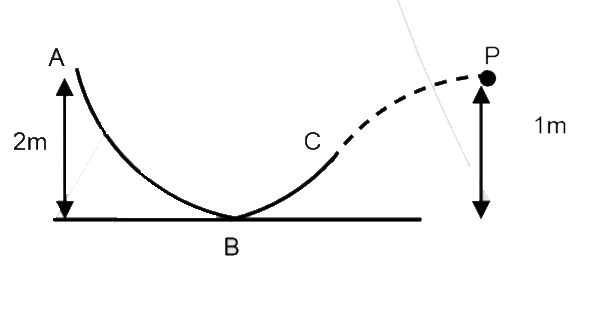
- A particle is released at point A. Find Kinetic energy at point P Give...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is exeuting SHM . At a point x = A//3 , kinetic energy of t...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 4 kg moves between two points A and B on a smooth h...
Text Solution
|
- A particle mass m = 0.1 kg is released from rest from a point A of a w...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is dropped from height H. At a point its kinetic energy is ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is released at point A. Find Kinetic energy at point P Give...
Text Solution
|
- In the given question, let the charge be released from rest at point B...
Text Solution
|
- In the given question let the charge be released from rest at point B ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 1 kg is released from the top of a wedge of mass 2 kg....
Text Solution
|