Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
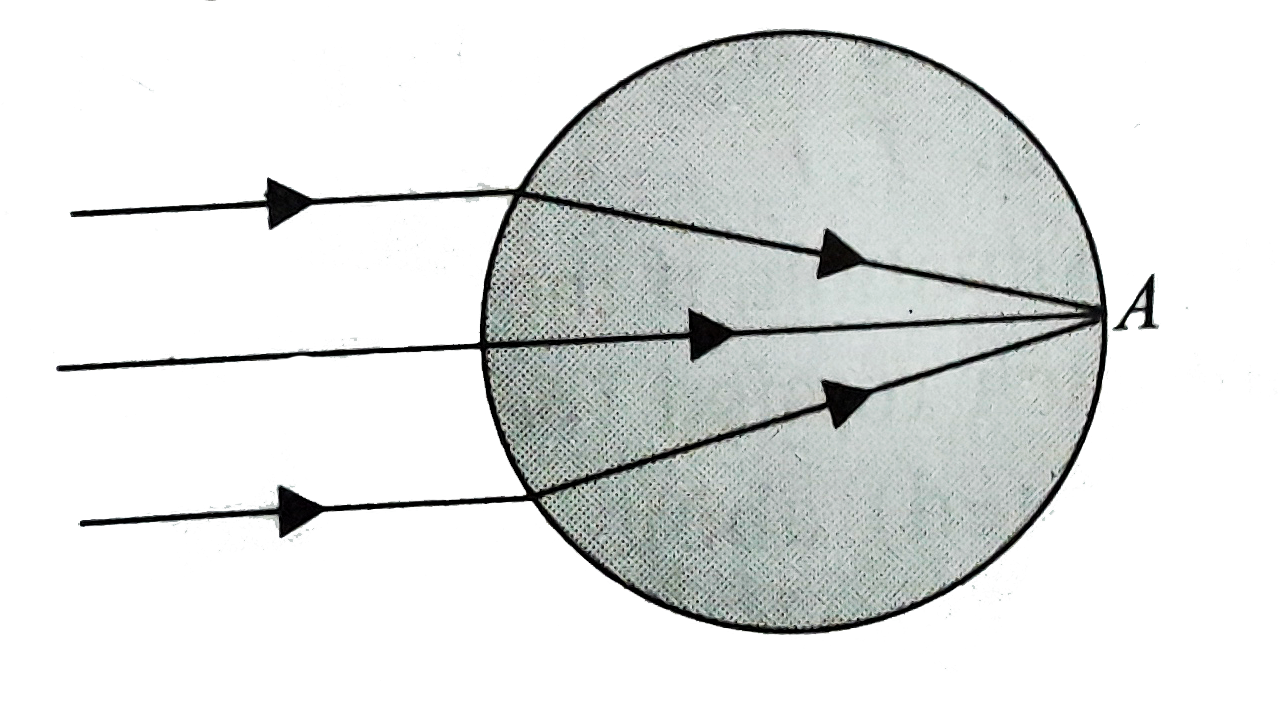
- A parallel beam of light falls on a solid tranparent sphere. Q. W...
Text Solution
|
- A perfectly reflecting solid sphere of radius r is kept in the path of...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius 1.00 cm is placed in the path of a parallel beam of...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light falls on a solid tranparent sphere. Q. Which ...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light falls on a solid tranparent sphere. Q. I...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light falls on a solid tranparent sphere. Q. For wh...
Text Solution
|
- In the path of a uniform light beam of large cross-sectional area and ...
Text Solution
|
- A narror parallel beam of light is incident paraxially on a solid tr...
Text Solution
|
- प्रकाश की एक पतली समानांतर बीम r त्रिज्या के एक पारदर्शी गोले पर लंबवत...
Text Solution
|