Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
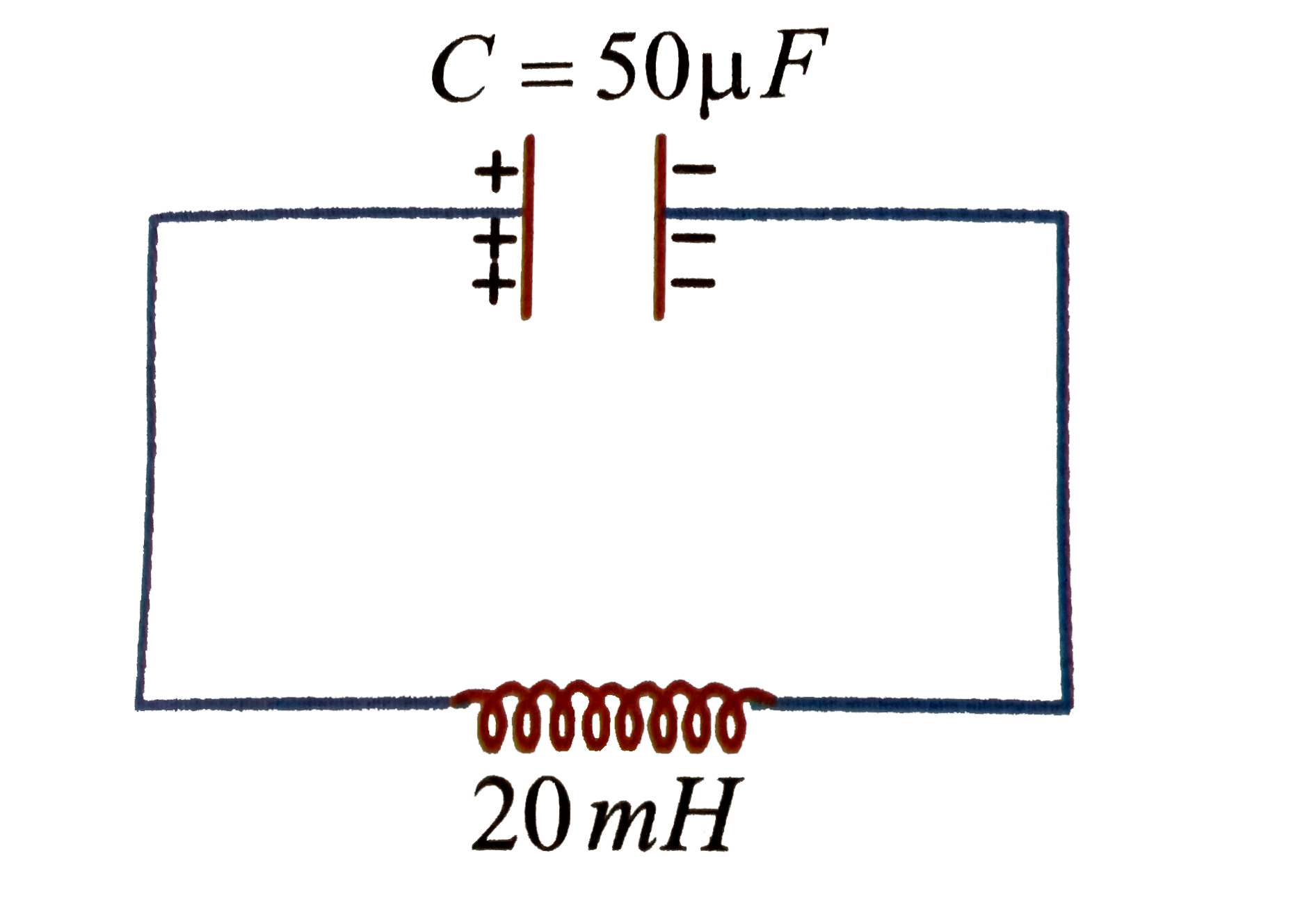
- An LC circuit contains a 20 mH inductor asn a 50 mu F capacitor with i...
Text Solution
|
- An LC circuit contains a 20 mH inductor asn a 50 mu F capacitor with i...
Text Solution
|
- An LC circuit contains a 20 mH inductor and a 50 mu F capacitor with a...
Text Solution
|
- किसी LC परिपथ में 20 mH का एक प्रेरक तथा 50 mu F का एक संधारित्र है जि...
Text Solution
|
- An LC circuit contains a 20 mH inductor and a 50 muF capacitor with an...
Text Solution
|
- An LC circuit contains a 20 mH inductor and a 50 muF capacitor with an...
Text Solution
|
- An LC circuit contains a 20 mH inductor and a 50 muF capacitor with an...
Text Solution
|
- An LC circuit contains a 20 mH inductor and a 50 muF capacitor with an...
Text Solution
|
- An LC circuit contains a 20 mH inductor and a 50 mu F capacitor with a...
Text Solution
|