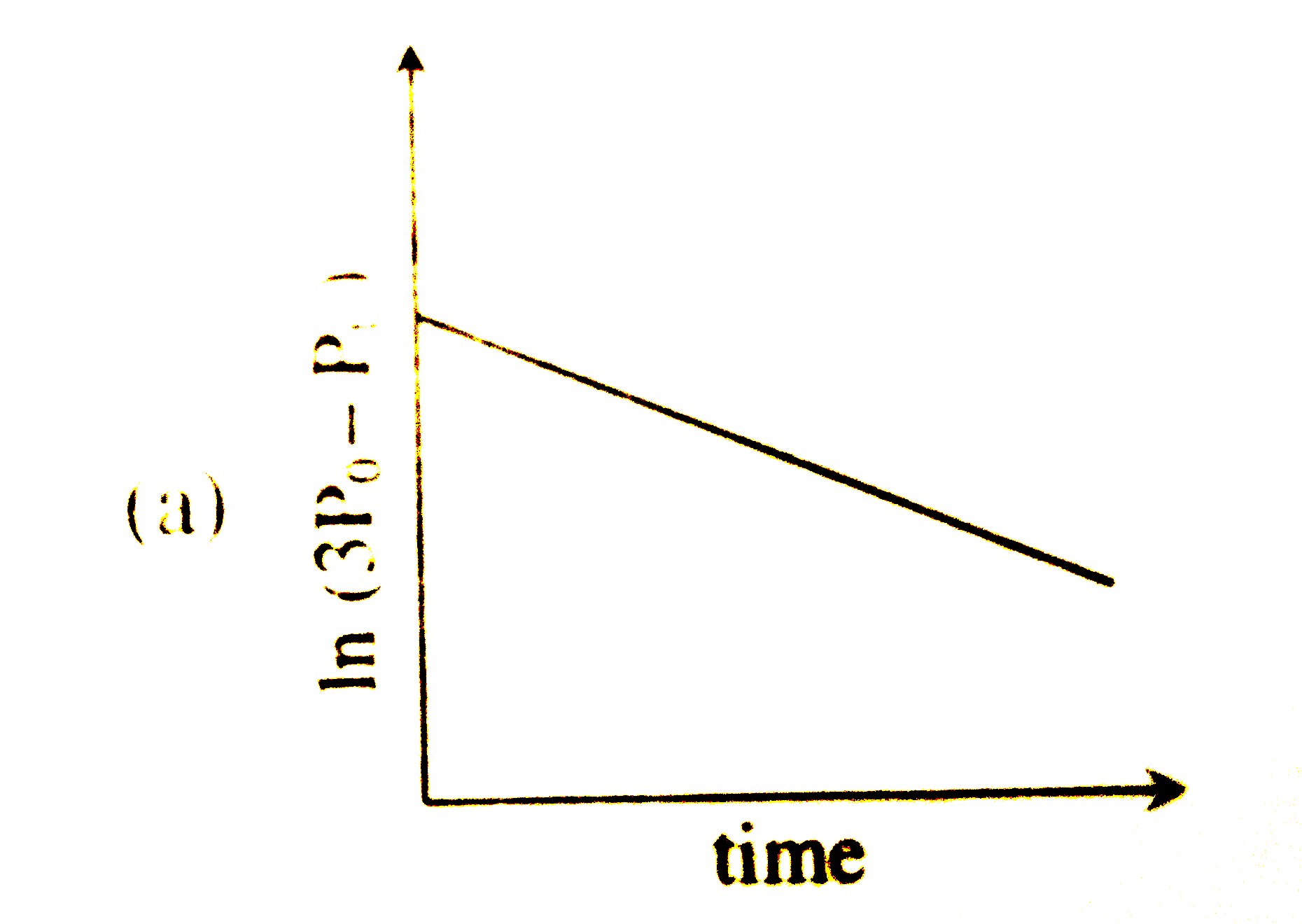
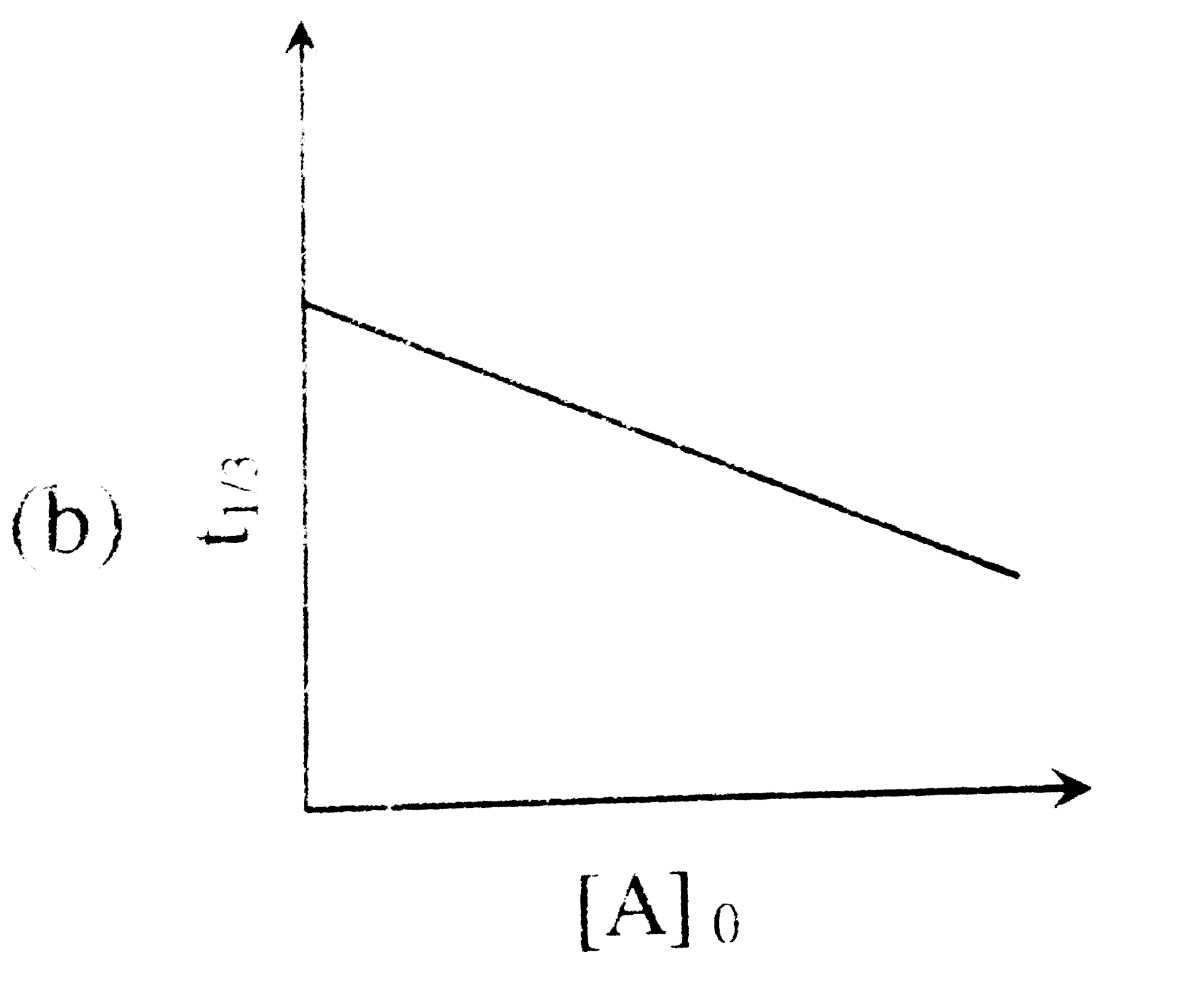
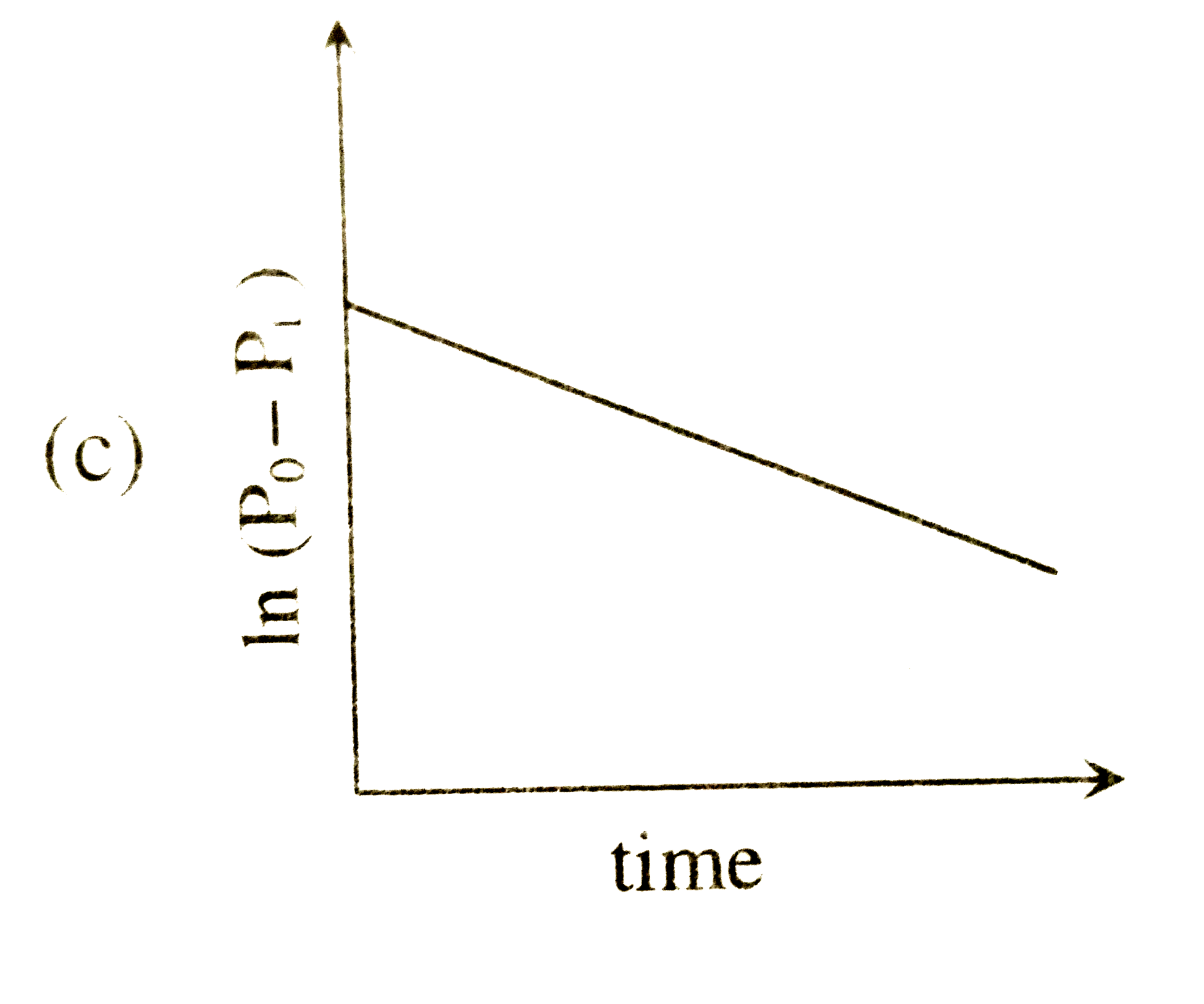
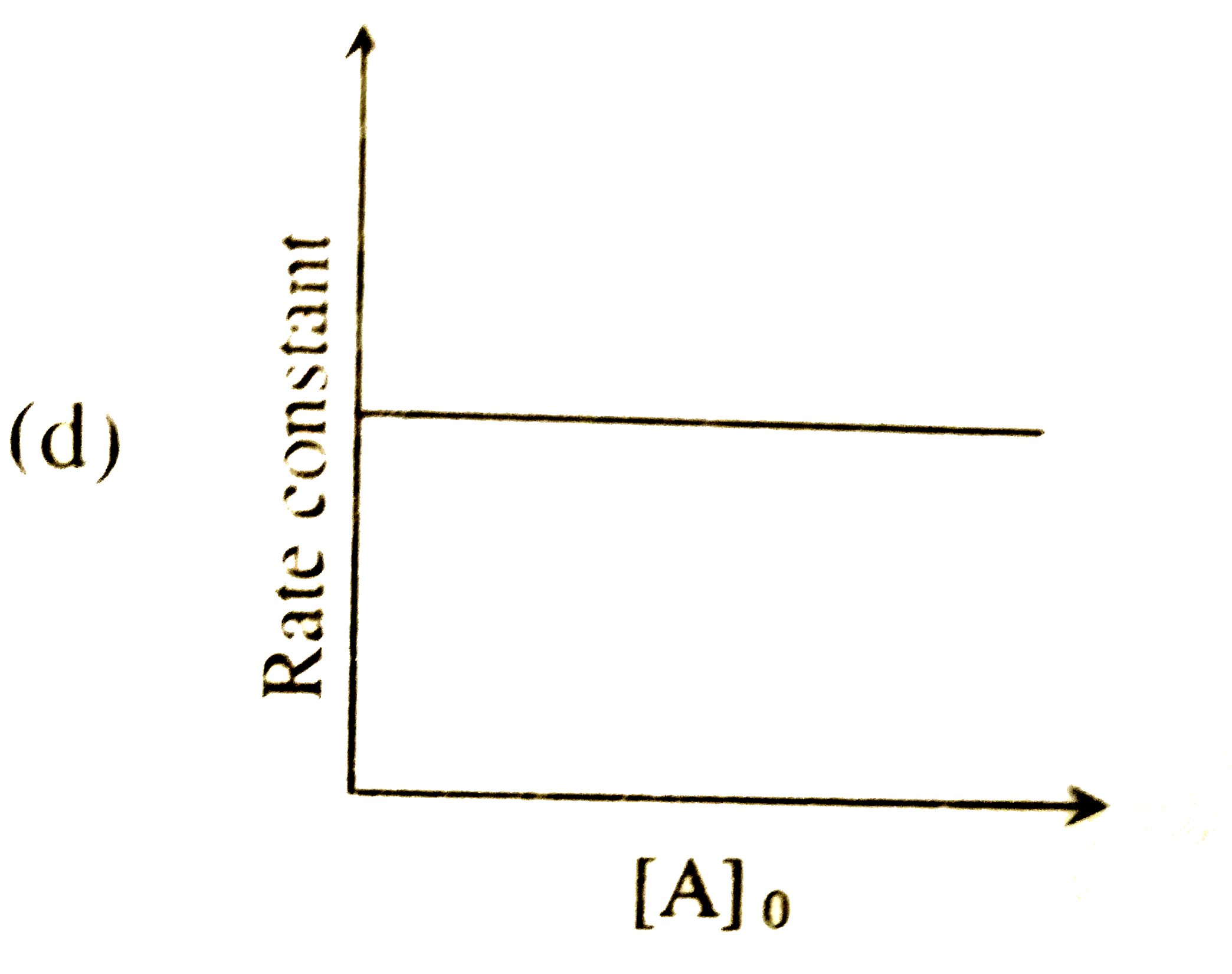
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- For a first order reaction A(g)rarr2B(g)+C(g) at constant volume and 3...
Text Solution
|
- In an elementary reaction A(g)+2B(g) to C(g) the initial pressure of A...
Text Solution
|
- For a first order reaction A(g) to 2B(g) + C(g) at constant volume and...
Text Solution
|
- For a first order reaction A(g)rarr2B(g)+C(g) at constant volume and 3...
Text Solution
|
- For a first order reaction A(g) to 2 B (g) + C(g) at constant volume a...
Text Solution
|
- For a first order gas phase reaction : A((g)) to 2B((g)) +C((g)) ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a first order gas phase decomposition reaction given below : ...
Text Solution
|
- A(g) rarr 2B(g)+C(g) Initially at t=0 gas A was present with some a...
Text Solution
|
- A(g) rarr 2B(g)+C(g) Initially at t=0 gas A was present with some a...
Text Solution
|