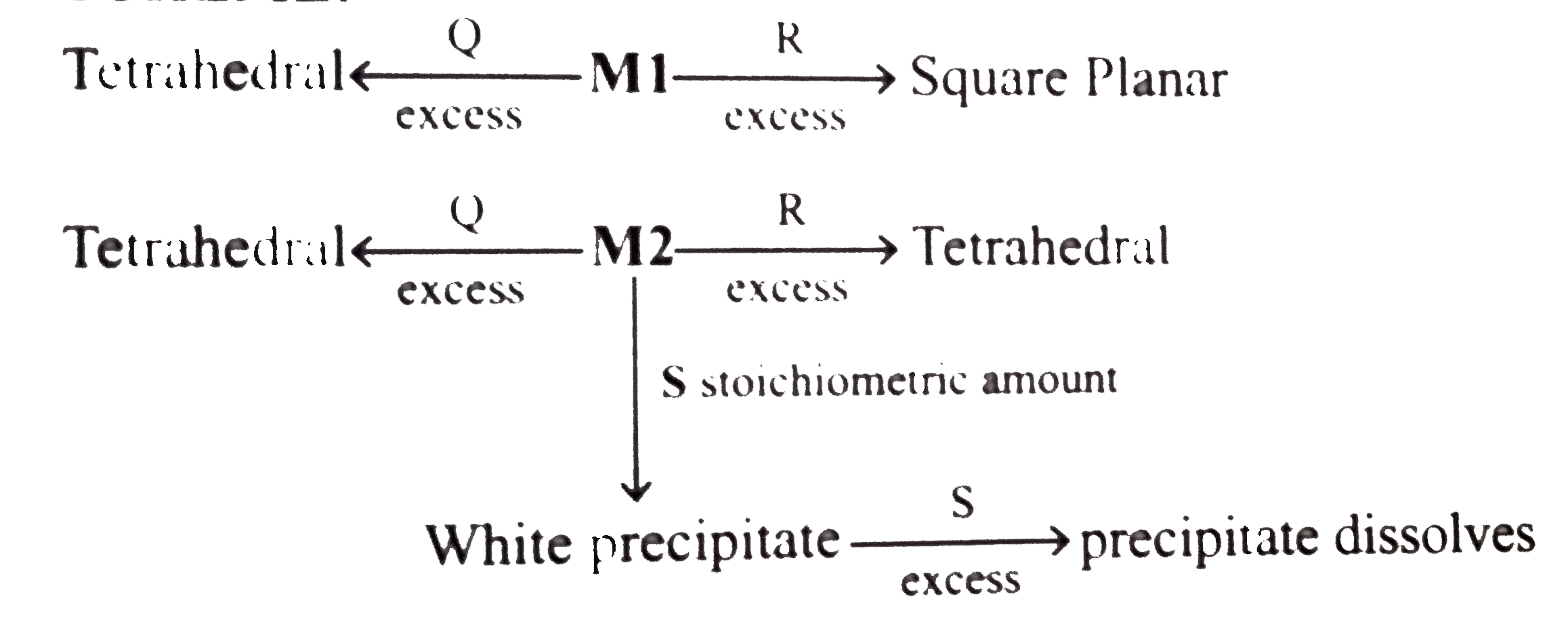
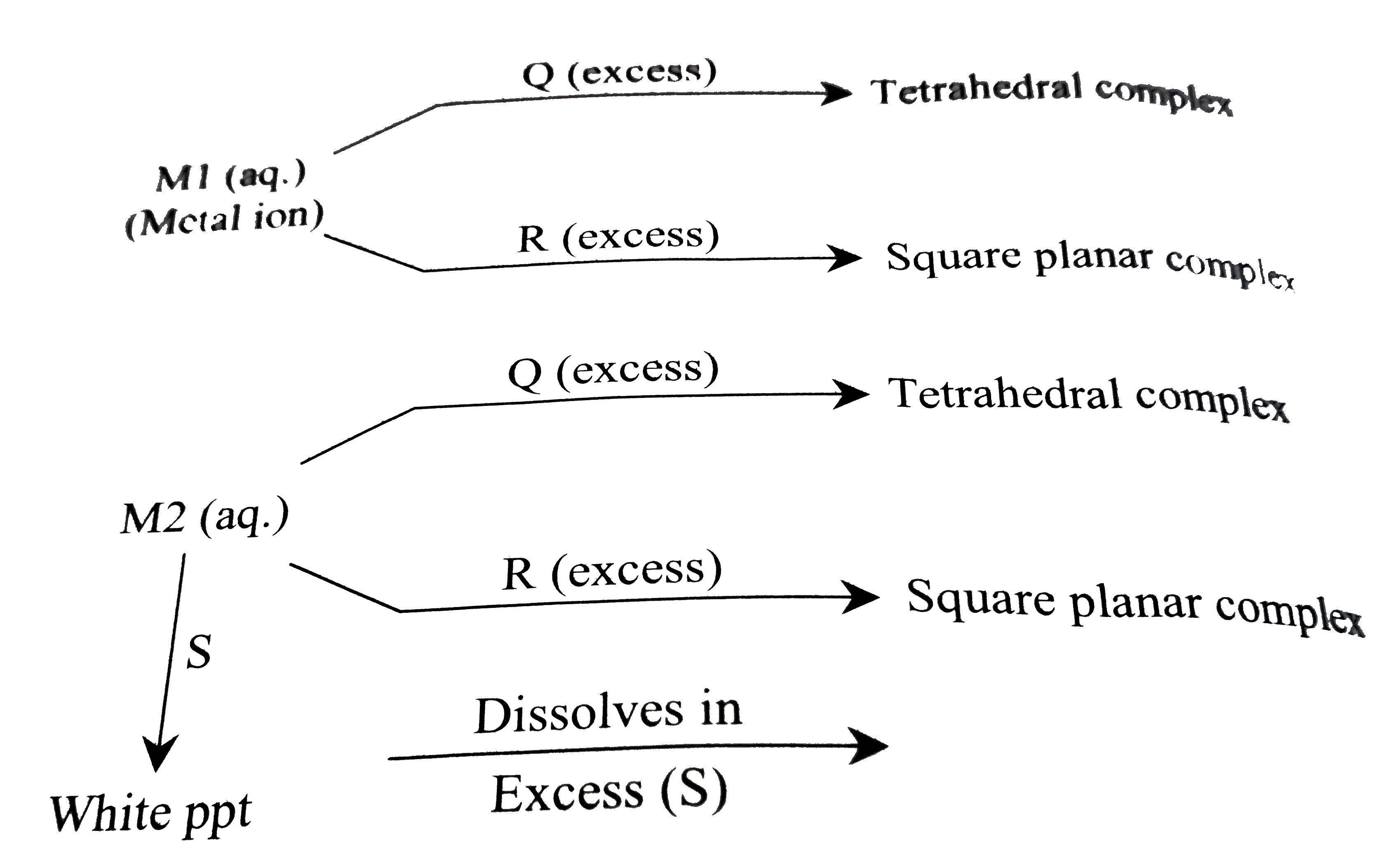
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- An aqueous solution of metal ion MI reacts separately with reagents Q ...
Text Solution
|
- An aqueous solution of metal ion MI reacts separately with reagents Q ...
Text Solution
|
- An aqueous solution of metal ion MI reacts separately with reagents Q ...
Text Solution
|
- An aqueous solution of a metal ion (A) on reaction with Kl gives a bla...
Text Solution
|
- An aqueous solution of metal ion M(1) reacts separately with reagents ...
Text Solution
|
- An aqueous solution of metal ion M(1) reacts separately with reagents ...
Text Solution
|
- An aqueous solution of metal ion M(1) reacts separately with reagents ...
Text Solution
|
- An aqueous solution of metal ion M(1) reacts separately with reagents ...
Text Solution
|
- In Aqueous solution, metal ion M(1) reacts separately with reagents Q ...
Text Solution
|