Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
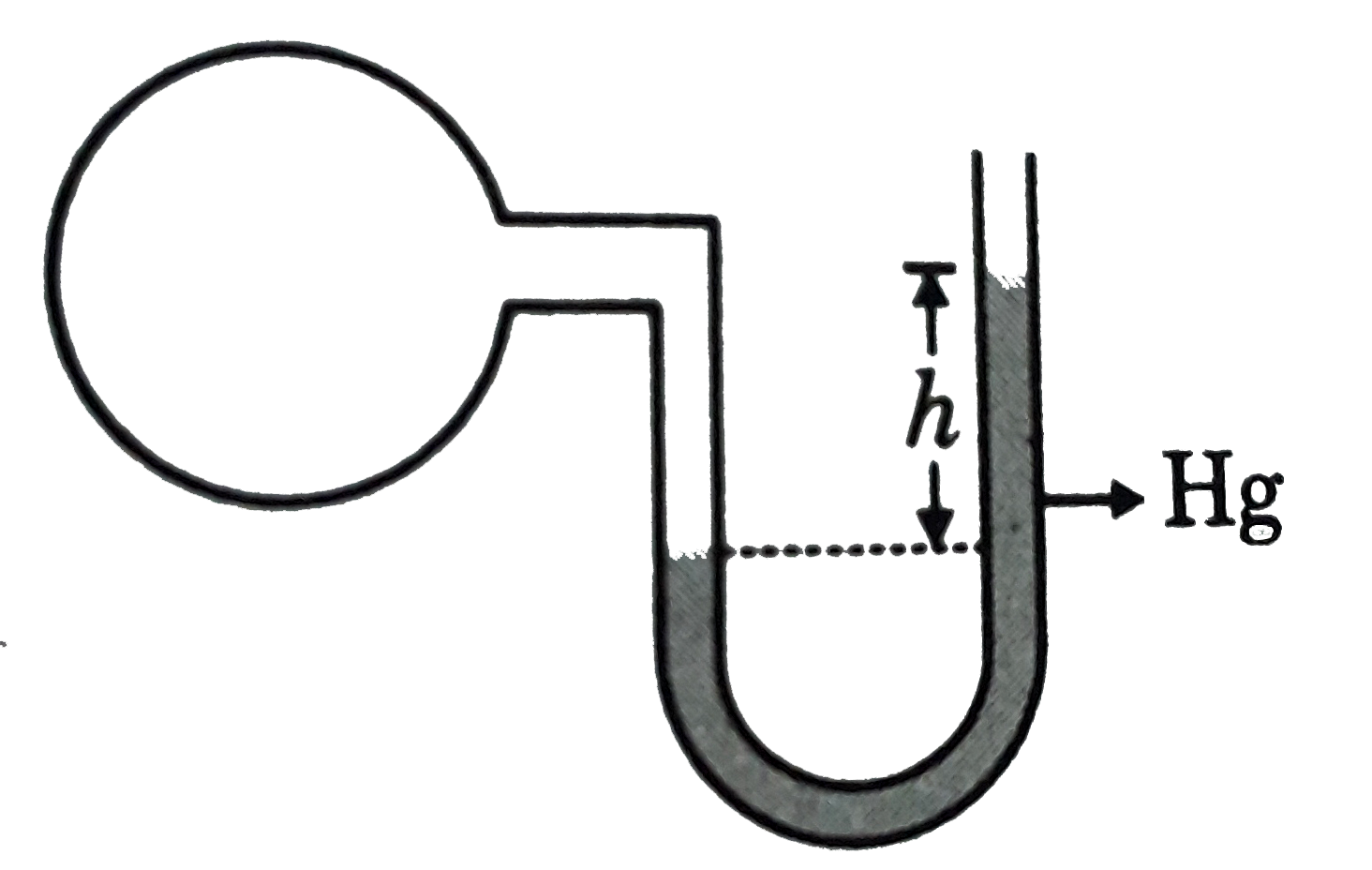
- A bulb of constant volume is attached to a very thin manometer tube as...
Text Solution
|
- A manometer is connected to a gas containing bulb. The open arm reads ...
Text Solution
|
- The pressure of a gas filled in the bulb of constant volume gas thermo...
Text Solution
|
- A bulb of constant volume is attached to a very thin manometer tube as...
Text Solution
|
- A bulb of constant volume is attached to a manometer tube open at othe...
Text Solution
|
- A manometer reads the pressure of a gas in an enclosure as shown in th...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र (a) में दर्शाए अनुसार कोई मैनोमीटर किसी बर्तन में भरी गैस के दाब...
Text Solution
|
- A bulb filled with a gas is connected to an open -end manometer. the l...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र (a) में दर्शाए अनुसार कोई मैनोमीटर किसी बर्तन में भरी गैस के दाब...
Text Solution
|