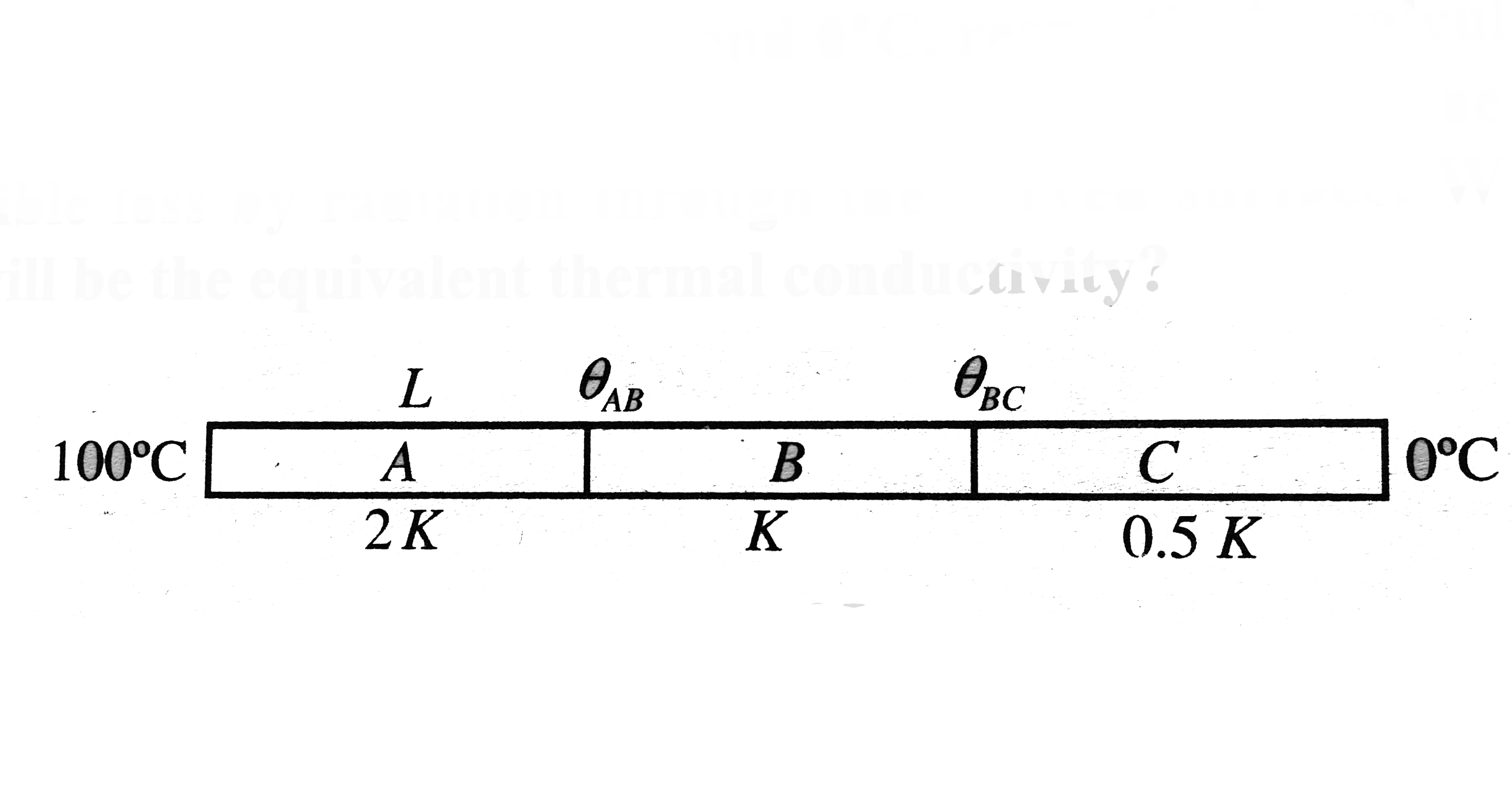Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Three cylindrical rods A, B and C of equal lengths and equal diameters...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods each of same length and cross - section are joined in serie...
Text Solution
|
- Three cylindrical rods A, B and C of equal lengths and equal diameters...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical rods are joined in series as shown. Their thermal cond...
Text Solution
|
- In a steady state of thermal conduction, temperature of the ends A and...
Text Solution
|
- Two similar rods are joined as shown in figure. Then temperature of ju...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of the same dimension have thermal conductivities 3K, 2K an...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of same dimensions have thermal conductivities 3K, 2k and K...
Text Solution
|
- Three rods of equal length, area of cross section and thermal conducti...
Text Solution
|