Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A rigid ball traveling in a straight line the x-axis hits a soled wall...
Text Solution
|
- A rigid ball traveling in a straight line the x-axis hits a soled wall...
Text Solution
|
- A player throws a ball upwards with an initail speed of 129.4 ms^(-1) ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball travelling in positive X direction with speed V0 hits a wall pe...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is released from point A. During its motion ball takes two seco...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 250 g moving with 20 m/s strikes a vertical wall and re...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 9.8 m/s from the g...
Text Solution
|
- If a ball is thrown vertically upward and the height 's' reached in ti...
Text Solution
|
- A player throws a ball upwards with an initial speed of 29.4 ms^(-1). ...
Text Solution
|
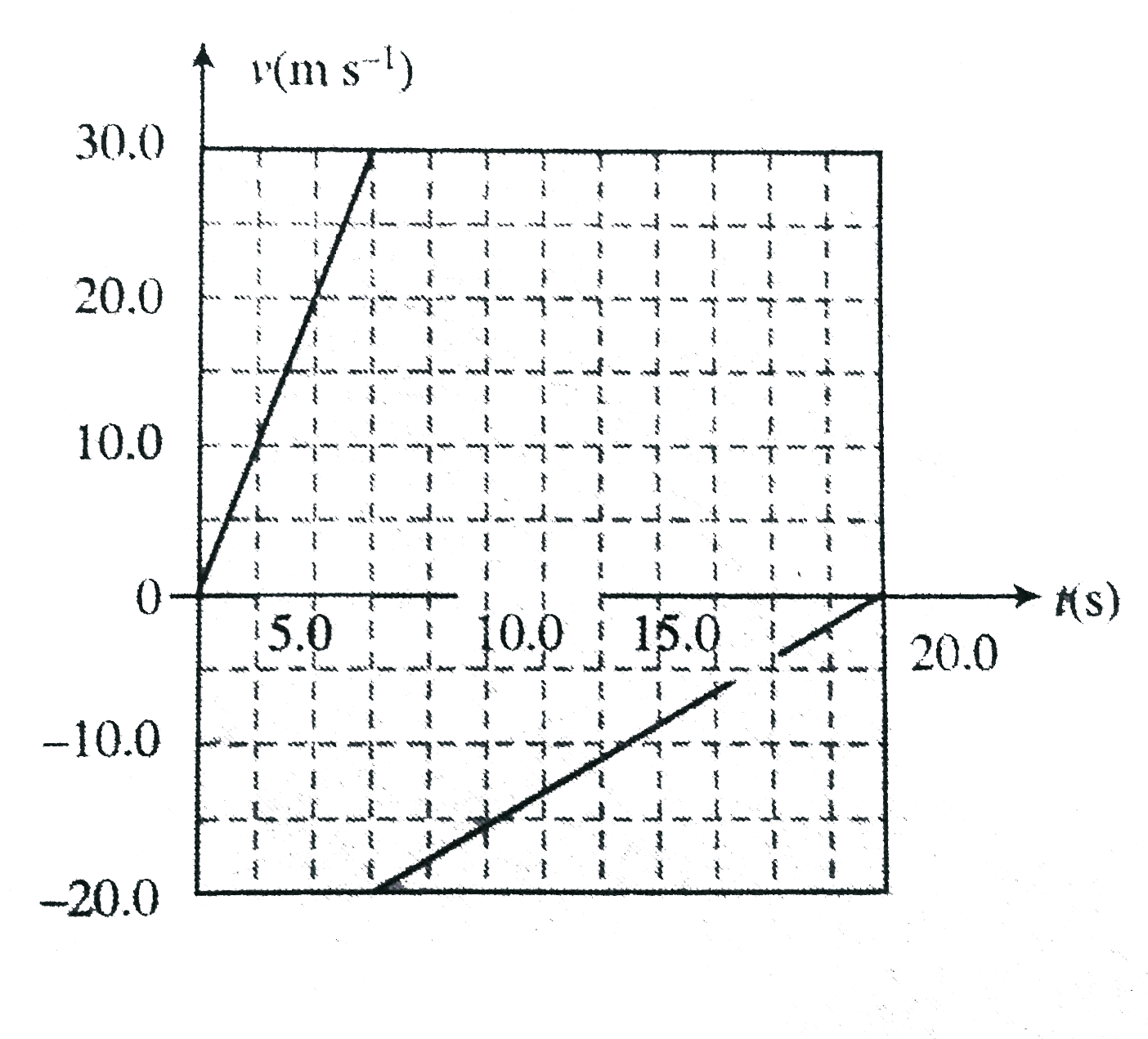 .
.