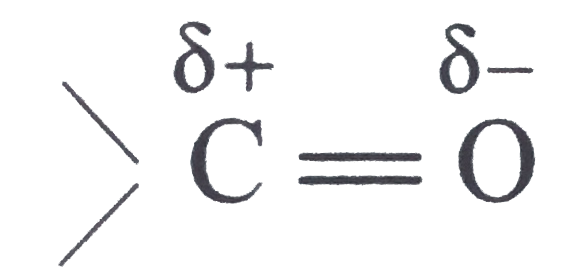Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Aldehydes and ketones ar specially susecptible to nucleophilic additio...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehyde and ketones are specially susceptible susceptible to nucleoph...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehyde and ketones are specially susceptible susceptible to nucleoph...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehyde and ketones are specially susceptible susceptible to nucleoph...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehyde and ketones are specially susceptible susceptible to nucleoph...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehyde and ketones are specially susceptible susceptible to nucleoph...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehydes and ketones ar specially susecptible to nucleophilic additio...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehydes and ketones ar specially susecptible to nucleophilic additio...
Text Solution
|
- Aldehydes and ketones ar specially susecptible to nucleophilic additio...
Text Solution
|
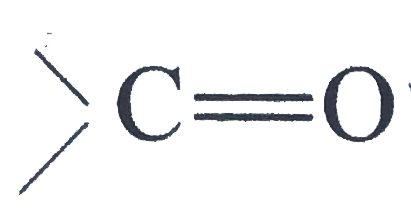 is polar (due to electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen)
is polar (due to electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen)