Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
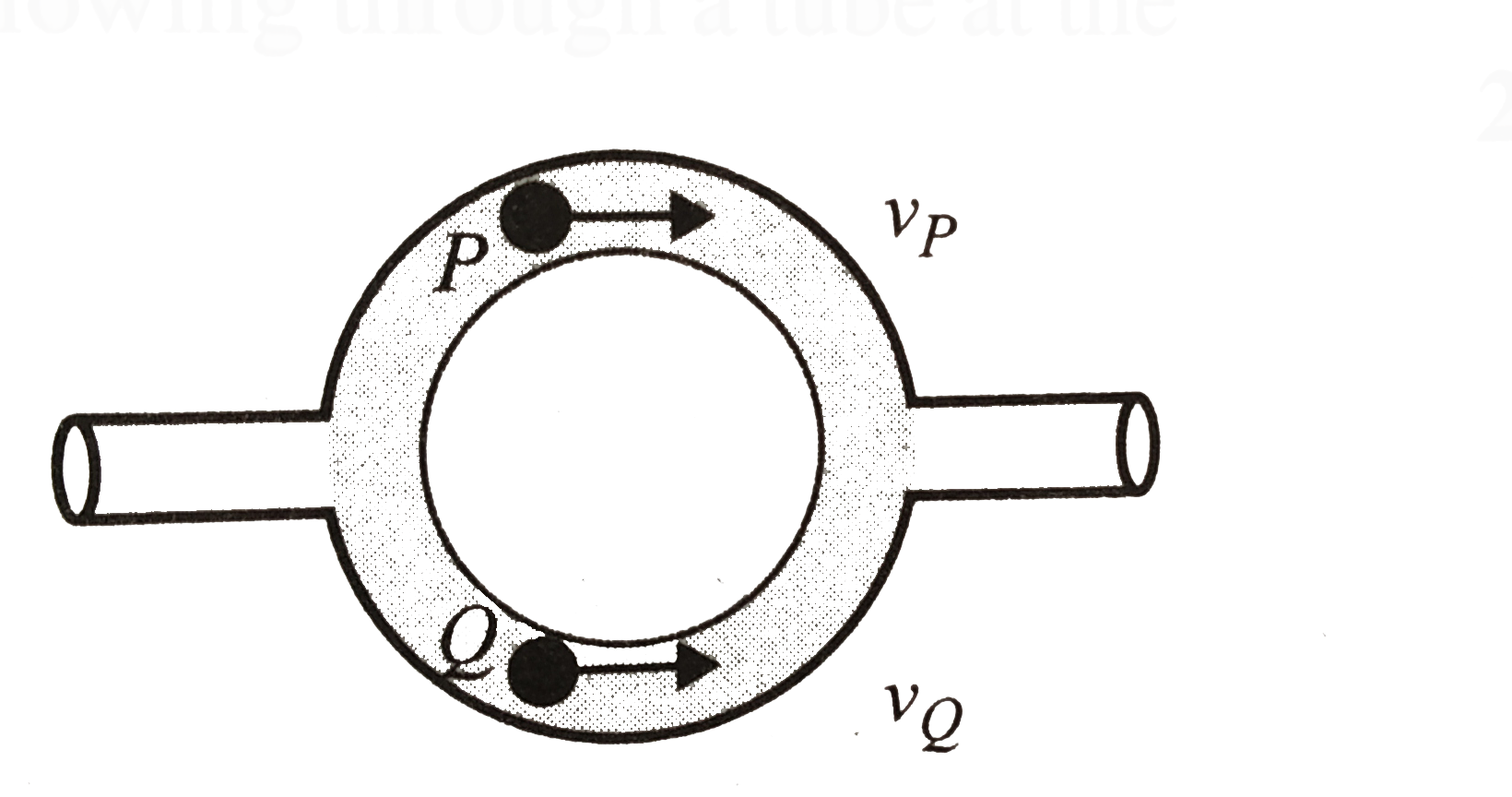
- Figure shows a liquid flowing through a tube at the rate of 0.1 m^(3)/...
Text Solution
|
- A non-viscous liquid of constant density 1000kg//m^3 flows in a stream...
Text Solution
|
- A non-viscous liquid of constant density 500 kg//m^(3) flows in a vari...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a liquid flowing through a tube at the rate of 0.1 m^(3)/...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid flows through a horizontal tube as shown in figure. The veloc...
Text Solution
|
- A non viscous liquid of constant density 10^(3) kg//m^(3) flows in str...
Text Solution
|
- If cross- sectional area of limb I is A(1) and that of limb II is A(2)...
Text Solution
|
- How does the pressure of liquid depend on the area 'of cross section o...
Text Solution
|
- According to the arrangement of Figure 3.48, a tube is divided into se...
Text Solution
|