Observed and calculated values for the standard electrode potentials of elements from Ti to Zn in the first reactivity series are depicted in figure (1):
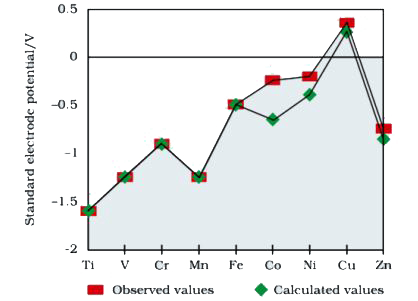
Explain the following observations:
i. The general trend towards less negative `E^(@)` values across the series
ii. The unique behaviour of Copper
iii. More negative `E^(@)` values of Mn and Zn
Observed and calculated values for the standard electrode potentials of elements from Ti to Zn in the first reactivity series are depicted in figure (1):

Explain the following observations:
i. The general trend towards less negative `E^(@)` values across the series
ii. The unique behaviour of Copper
iii. More negative `E^(@)` values of Mn and Zn

Explain the following observations:
i. The general trend towards less negative `E^(@)` values across the series
ii. The unique behaviour of Copper
iii. More negative `E^(@)` values of Mn and Zn
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
(a) What is meant by the term lanthanoid contraction ? What is it due to and what consequences does it have on the chemistry of elements following lanthanoids in the periodic table ? (b) Explain the following observations : (i) Cu^(+) ion is unstable in aqueous solutions . (ii) Although Co^(2+) ion appears to be stable , it is easily oxidised to Co^(3+) ion in the presence of a strong ligand. (iii) The E_(Mn^(2+)//Mn)^(@) value for manganese is much more than expected from the trend for other elements in the series.
(a) What is meant by the term lanthanoid contraction ? What is it due to and what consequences does it have on the chemistry of elements following lanthanoids in the periodic table ? (b) Explain the following observations : (i) Cu^(+) ion is unstable in aqueous solutions . (ii) Although Co^(2+) ion appears to be stable , it is easily oxidised to Co^(3+) ion in the presence of a strong ligand. (iii) The E_(Mn^(2+)//Mn)^(@) value for manganese is much more than expected from the trend for other elements in the series.
The potential associated with each electrode is known as electrode potential. If the concentration of each species taking part in the electrode reaction is unity (if any appears in the electrode reaction, it is confined to 1 atmospheric pressure) and further the reaction is carried out at 298 K, then the potential of each electrode is said to the standard electrode potential. By convention, the standard electrode potential of hydrogen electrode is 0.0 volt. The electrode potential value for each electrode process is a measure of relative tendency of the active species in the process to remain in the oxidised/reduced form. A negative E^(@) means that the redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H^(+)//H_(2) couple. A positive E^(@) means that the redox couple is a weaker reducing agent than the H^(+)//H_(2) couple. The metal with greater positive value of standard reduction potential forms the oxide of greater thermal stability. Which of the following couples will have highest value of emf ?
The potential associated with each electrode is known as electrode potential. If the concentration of each species taking part in the electrode reaction is unity (if any appears in the electrode reaction, it is confined to 1 atmospheric pressure) and further the reaction is carried out at 298 K, then the potential of each electrode is said to the standard electrode potential. By convention, the standard electrode potential of hydrogen electrode is 0.0 volt. The electrode potential value for each electrode process is a measure of relative tendency of the active species in the process to remain in the oxidised/reduced form. A negative E^(@) means that the redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H^(+)//H_(2) couple. A positive E^(@) means that the redox couple is a weaker reducing agent than the H^(+)//H_(2) couple. The metal with greater positive value of standard reduction potential forms the oxide of greater thermal stability. Which of the following couples will have highest value of emf ?
The potential associated with each electrode is known as electrode potential. If the concentration of each species taking part in the electrode reaction is unity (if any appears in the electrode reaction, it is confined to 1 atmospheric pressure) and further the reaction is carried out at 298 K, then the potential of each electrode is said to the standard electrode potential. By convention, the standard electrode potential of hydrogen electrode is 0.0 volt. The electrode potential value for each electrode process is a measure of relative tendency of the active species in the process to remain in the oxidised/reduced form. A negative E^(@) means that the redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H^(+)//H_(2) couple. A positive E^(@) means that the redox couple is a weaker reducing agent than the H^(+)//H_(2) couple. The metal with greater positive value of standard reduction potential forms the oxide of greater thermal stability. Which of the following reactions is not correct ?
The potential associated with each electrode is known as electrode potential. If the concentration of each species taking part in the electrode reaction is unity (if any appears in the electrode reaction, it is confined to 1 atmospheric pressure) and further the reaction is carried out at 298 K, then the potential of each electrode is said to the standard electrode potential. By convention, the standard electrode potential of hydrogen electrode is 0.0 volt. The electrode potential value for each electrode process is a measure of relative tendency of the active species in the process to remain in the oxidised/reduced form. A negative E^(@) means that the redox couple is a stronger reducing agent than the H^(+)//H_(2) couple. A positive E^(@) means that the redox couple is a weaker reducing agent than the H^(+)//H_(2) couple. The metal with greater positive value of standard reduction potential forms the oxide of greater thermal stability. Which of the following reactions is not correct ?
Recommended Questions
- Observed and calculated values for the standard electrode potentials o...
Text Solution
|
- Why E^(-) values for Mn, Ni and Zn are more negative than expected?
Text Solution
|
- Following are the values of standard potentials of two half cells, whi...
Text Solution
|
- Why E^(@) value of Mn, Ni and Zn are more negative than expected ?
Text Solution
|
- Why E^(@) values for Mn, Ni and Zn are more negative than expected ?
Text Solution
|
- Why do Mn, Ni and Zn exhibit more negative E^(Theta) values than expec...
Text Solution
|
- 3d संक्रमण श्रेणी के तत्व नीचे दिये गये है - Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni ...
Text Solution
|
- Why standard reduction potential (E^(0)) of Zn^(2+)|Zn system is more ...
Text Solution
|
- Why E^(0) values for Mn, Ni and Zn are more negative than expected ?
Text Solution
|