Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
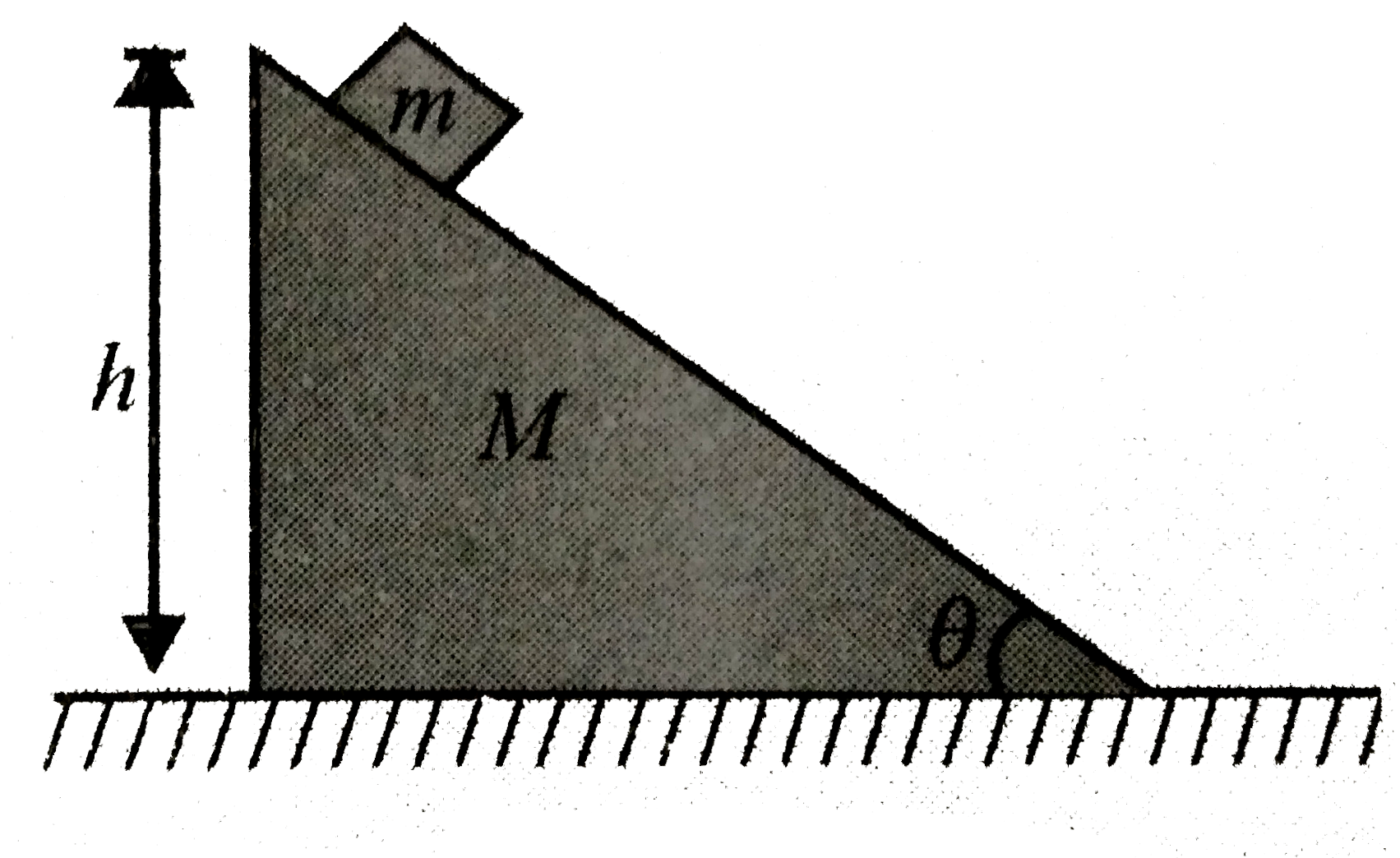
- A block of mass m is initially lying on a wedge of mass M with an angl...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth block of mass m is held stationary on a smooth wedge of mass ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is released from the top of a wedge of mass M as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on the inclined sufrace of a wedge as show...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is initially lying on a wedge of mass M with an angl...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth inclined wedge ABC of inclinat...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m slides down on inclined wedge of same mass m as show...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is released from a wedge of mass m as shown in figur...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth inclined wedge ABC of inclinat...
Text Solution
|