Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
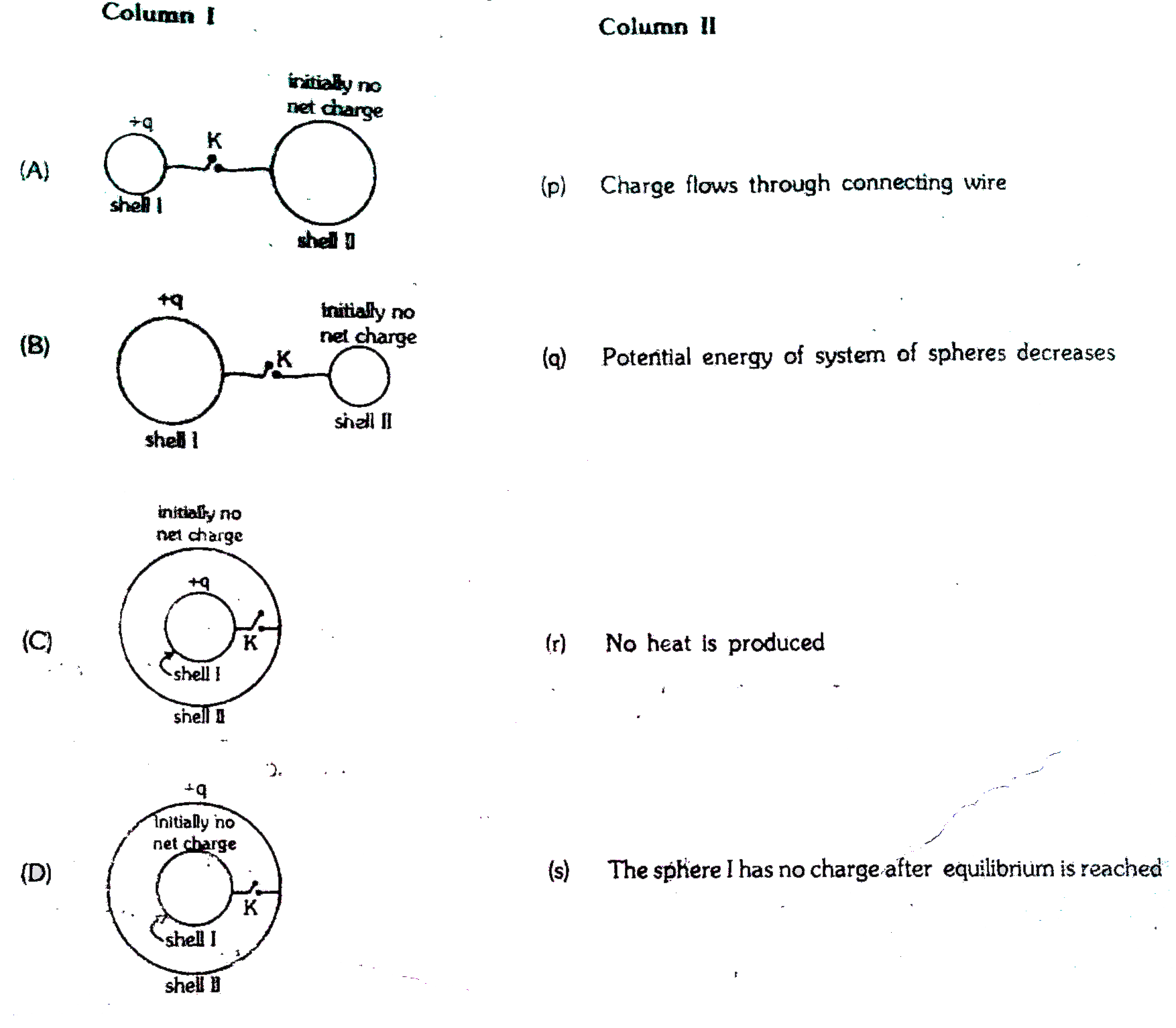
- Column-I gives certain situations involving two thin conducting shells...
Text Solution
|
- A solid conducting sphere of radius a has a net positive charge 2Q. A ...
Text Solution
|
- Charge q on a small conducting sphere S(1) is placed inside a large ho...
Text Solution
|
- Column-I gives certain situations involving two thin conducting shells...
Text Solution
|
- There are three concentric conducting spherical shells. All of them ar...
Text Solution
|
- The circuit involves two ideal cells connected to a 1 mu F capacitor v...
Text Solution
|
- Column I gives certain situations involving two thin conducting shells...
Text Solution
|
- The net charge given to an isolated conducting solid sphere :
Text Solution
|
- Two metallic spheres of radii a and b are placed faraway from each oth...
Text Solution
|