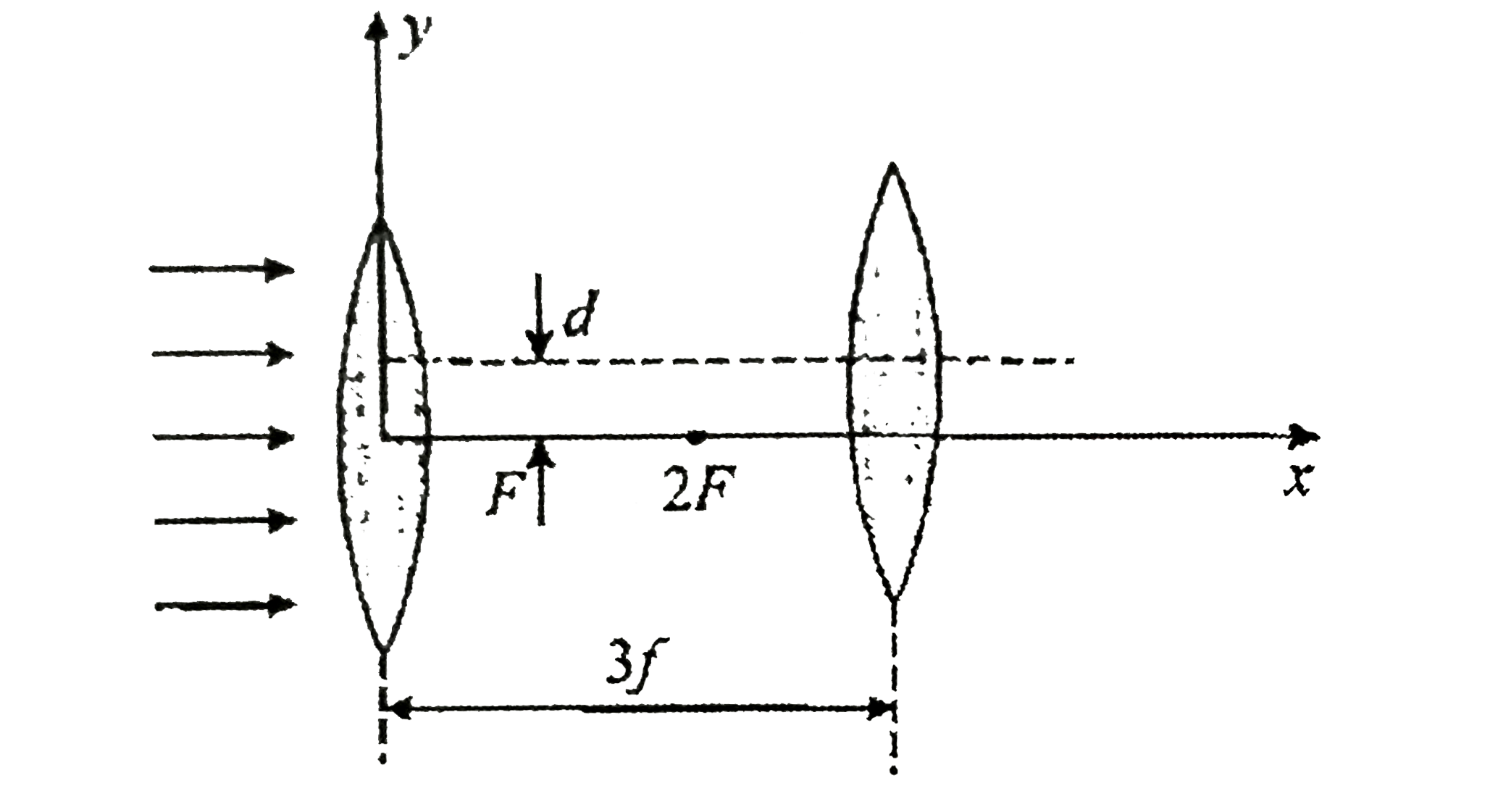Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In the figure- it is shown,the focal length f of the two thin convex l...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin convex lenses of focal lengths f(1) and f(2) are separated by...
Text Solution
|
- If the optic axis of convex and concave lenses are separated by a dist...
Text Solution
|
- Two converging lenses of the same focal length f are separated by a di...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a coaxial system of two thin convex lenses of focal length f ...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length f cut into parts first horizontally and ...
Text Solution
|
- This question concerna a symmetrical lens shown, along with its two fo...
Text Solution
|
- the focal length of the two thin convex lenses is the same =f They are...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin convex lenses of focal lengthf(1)andf(2)are separated by a ho...
Text Solution
|