Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
FORCE AND MOTION - I
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise CHECKPOINT|5 VideosFORCE AND MOTION - I
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PROBLEMS|52 VideosFLUIDS
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type )|5 VideosFORCE AND MOTION-II
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY-FORCE AND MOTION - I -PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)
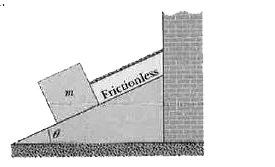
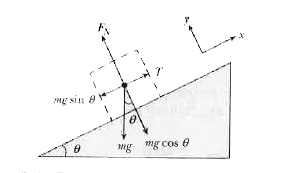
- In Fig. 5-27, a block attached to a chord is resting on an inclined pl...
Text Solution
|
- An elevator starts from rest with a constant upward acceleration. It m...
Text Solution
|
- Workers are loading equipment into a freight elevator at the top floor...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks A, B and C of masses 5 kg, 10 kg and 15 kg respectively c...
Text Solution
|