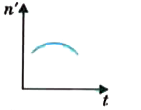
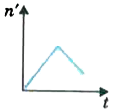
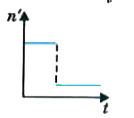
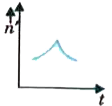
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WAVES
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise HIGH ORDER THINKING SKILLS & ADVANCED LEVEL|15 VideosWAVES
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise REVISION EXERCISES|107 VideosWAVES
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT ADDITIONAL EXERCISES|6 VideosUNITS AND MEASUREMENT
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST|15 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Chapter Practice Test|16 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-WAVES-NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS
- Equation of a plane progressive wave is given by y=0.6 sin 2pi(t-(x)/(...
Text Solution
|
- A string of mass 2.50kg is under a tension os 200N. The length of the ...
Text Solution
|
- A train whistling at constant frequency is moving towards a station at...
Text Solution
|
- A transverse harmonic wave on a string is descrbed by y(x, t) = 3.0 si...
Text Solution
|
- The displacement of a string is given by y(x,t)=0.06sin(2pix//3)cos(12...
Text Solution
|
- Speed of sound waves in a fluid depends
Text Solution
|
- During propagation of a plane progressive mechanical wave,
Text Solution
|
- The transverse displacement of a string (clamped at its both ends ) is...
Text Solution
|
- A train, standing in a station yard, blows a whistle of frequency 400H...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are true for a stationary wave ?
Text Solution
|
- A sonometer wire is vibrating is resonance with a tuning fork. Keeping...
Text Solution
|
- An organ pipe of length L open at both ends is found to vibrate in its...
Text Solution
|
- A tuning fork A, marked 512 Hz, produces 5 beats per second, when soun...
Text Solution
|
- The displacement of an elastic wave is given by the function y=3 sin o...
Text Solution
|
- A sitar wire is replaced by another wire of same length and material b...
Text Solution
|
- At what temperatures (i n ^(@)C) will the speed of sound in air be 3 t...
Text Solution
|
- When two waves of almost equal frequencies n(1) andn(2) reach at a po...
Text Solution
|
- A steel wire has a length of 12 m and a mass of 2.10 kg. What will be ...
Text Solution
|
- A pipe 20 cm long is closed at one end. Which harmonic mode of the pip...
Text Solution
|
- A train standing at the outer signal of a railway station blows a whis...
Text Solution
|