Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
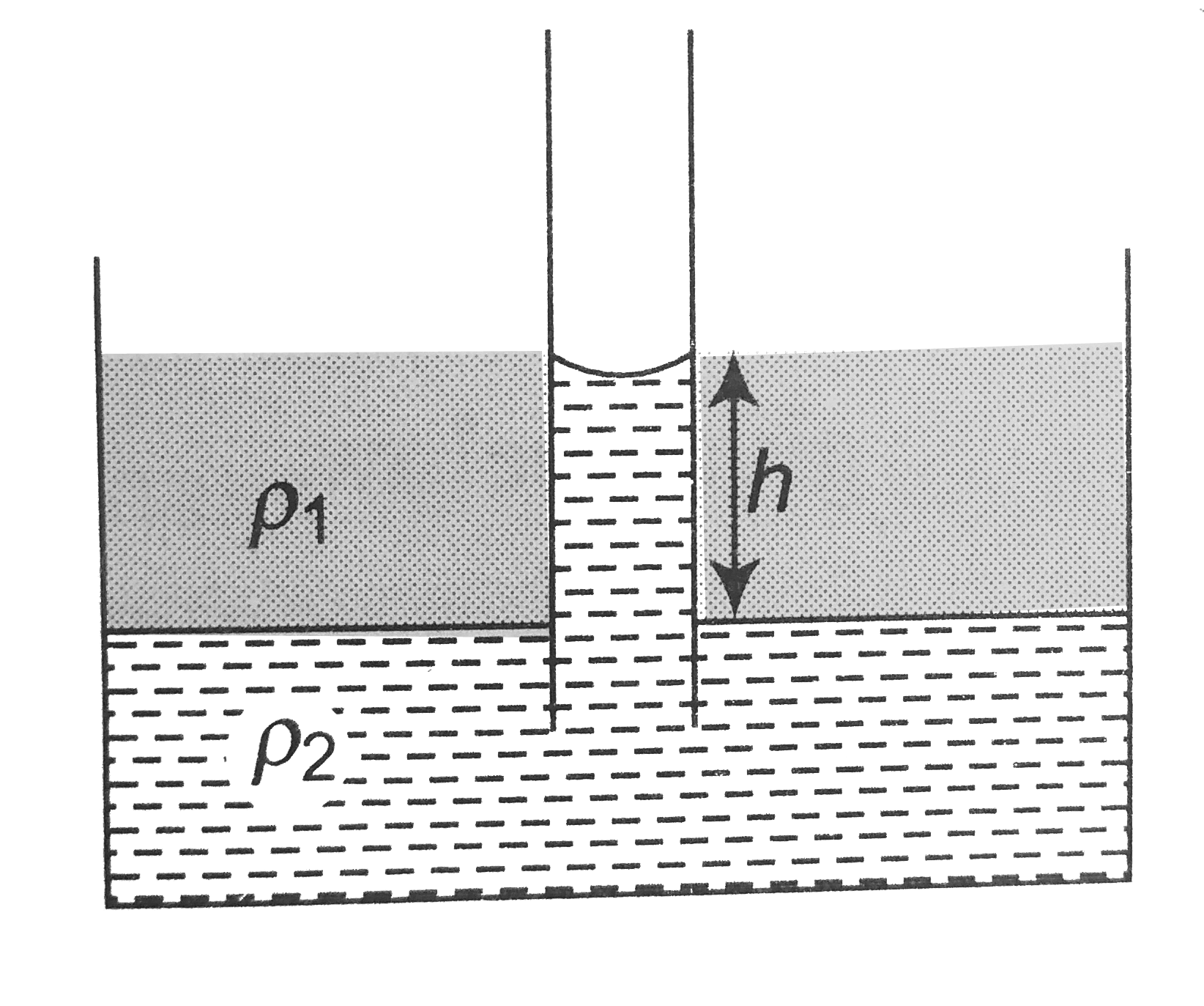
- A container is partially filled with a liquid of density rho2 A capill...
Text Solution
|
- A container is partially filled with a liquid of density rho2 A capill...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid of density rho and surface tension S rises to a height h in a...
Text Solution
|
- When a capillary tube of radius r is immersed in a liquid of density r...
Text Solution
|
- A capillary tube of radius r is immersed vertically in a liquid such t...
Text Solution
|
- The end of a capillary tube is immersed into a liquid. Liquid slowly r...
Text Solution
|
- The height of liquid column in capillary tube is h the radius of capil...
Text Solution
|
- The radius of the bore of a capillary tube is r and the angle of conta...
Text Solution
|
- A liquid of density rho and surface tension sigma rises in a capillary...
Text Solution
|