Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
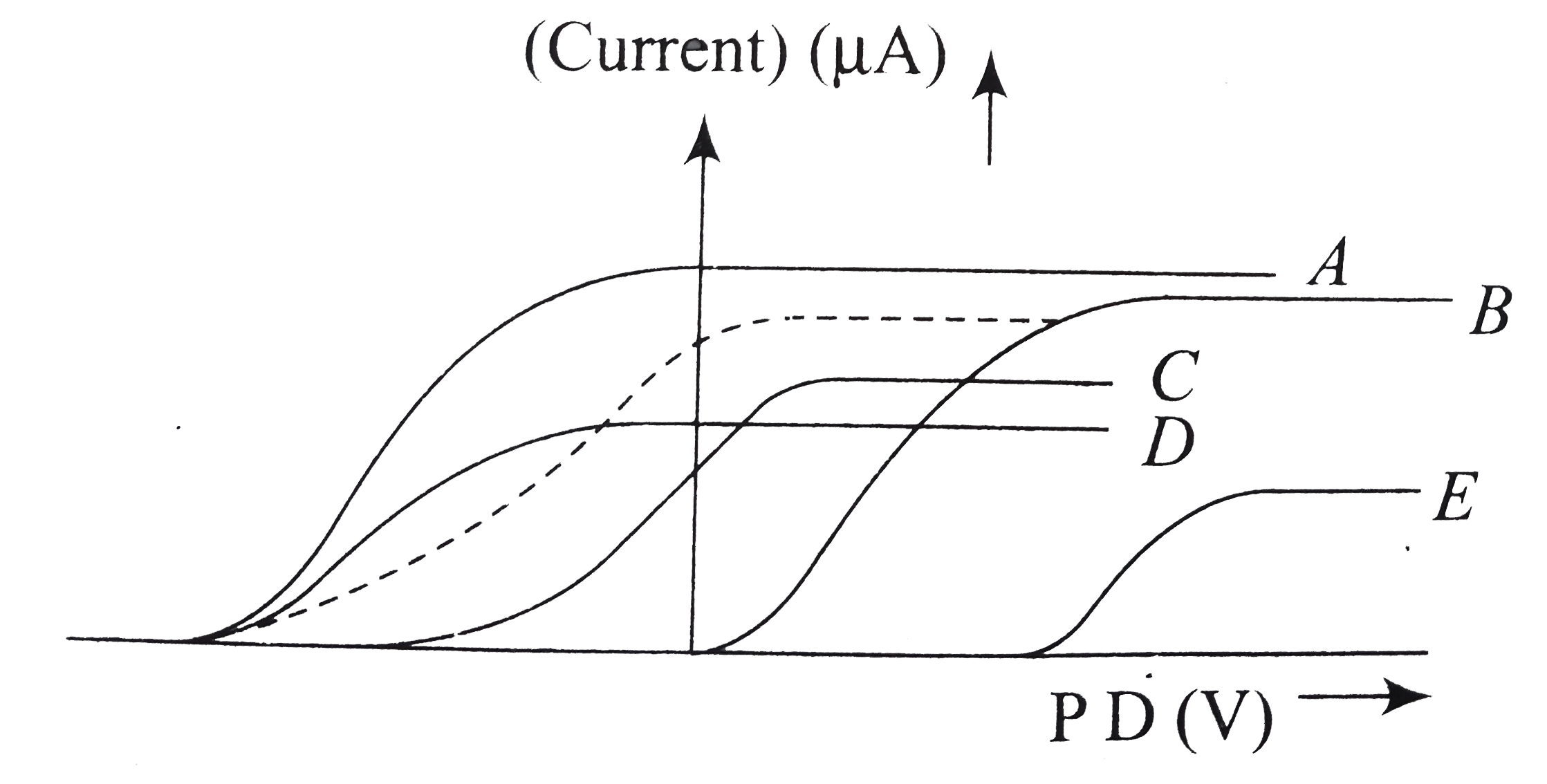
- A photoelectric cell is connected to a source of variable potential di...
Text Solution
|
- A photoelectric cell is connected to a source of variable potential di...
Text Solution
|
- The stopping potential as a function of the frequency of the incident ...
Text Solution
|
- Plot a graph showing the variation of photoelectric current with anode...
Text Solution
|
- In a plot of photoelectric current versus anode potential, how does ...
Text Solution
|
- A photoelectric cell is connected to a source of variable potential di...
Text Solution
|
- Darw graphs showing variation of photoelctric current with applied ...
Text Solution
|
- Light of intensity I and frequency v is incident on a photossensitive...
Text Solution
|
- Draw graphs showing variation of photoelectric current with applied vo...
Text Solution
|