Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT TAMIL-WORK, ENERGY AND POWER-EXERCISES (ADDITIONAL EXERCISES)
- A bullet of mass 0.012 kg and horizontal speed 70ms^(-1) strikes a blo...
Text Solution
|
- Two inclined frictionless tracks, one gradual and the other steep meet...
Text Solution
|
- A 1kg block situated on a rough incline is connected to a spring of sp...
Text Solution
|
- A bob of mass 0.3 kg falls from the ceiling of an elevator moving down...
Text Solution
|
- A (trolley + child) of total mass 200 kg is moving with a uniform spee...
Text Solution
|
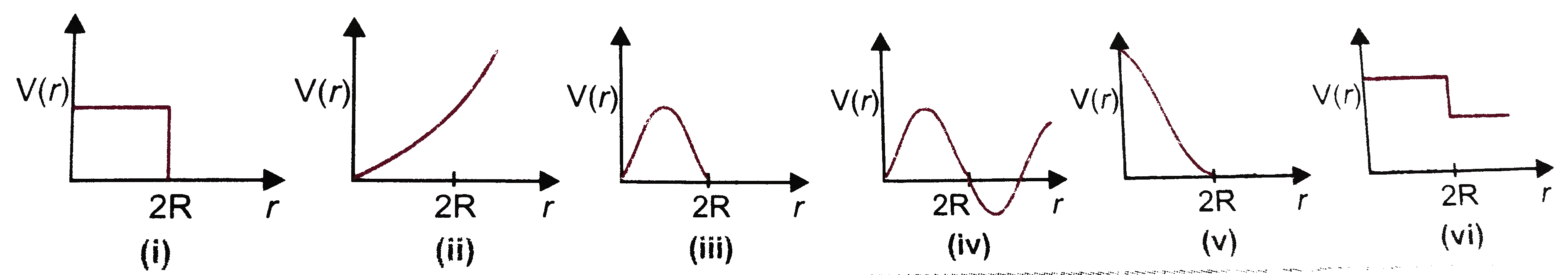
- Which of the following potential energy curves in figure., cannot poss...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the decay of a free neutron at rest: ntop+e^(-) Show that the...
Text Solution
|