Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A uniform disc is spun with an angular velocity omega and simultaneous...
Text Solution
|
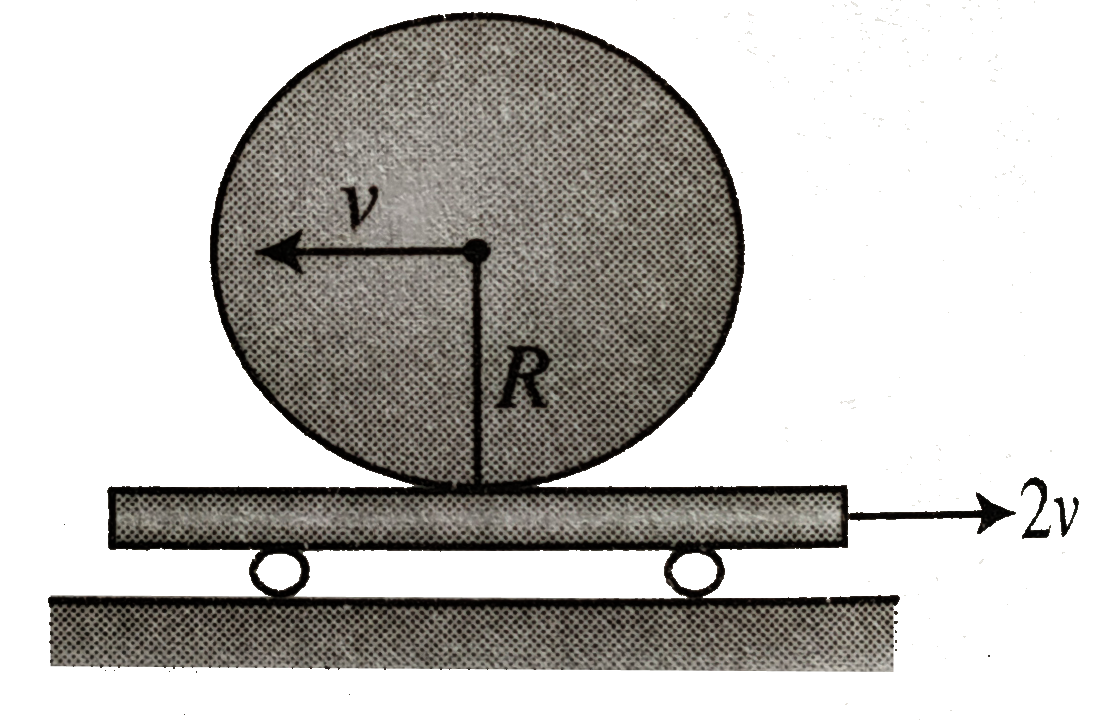
- A uniform disc of radius R rolls perfectly over two horizontal plank A...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder rolls on the planks A and B without relative sliding. If th...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc is spun with an angular velocity omega and simultaneous...
Text Solution
|
- A plank is moving on ground with a velocity v and a block is moving on...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of the radius R is confined to roll without slipping at A and B...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass M and radius R initially stands vertically on t...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass M and radius R initially stands vertically on t...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass M and radius R initially stands vertically on t...
Text Solution
|