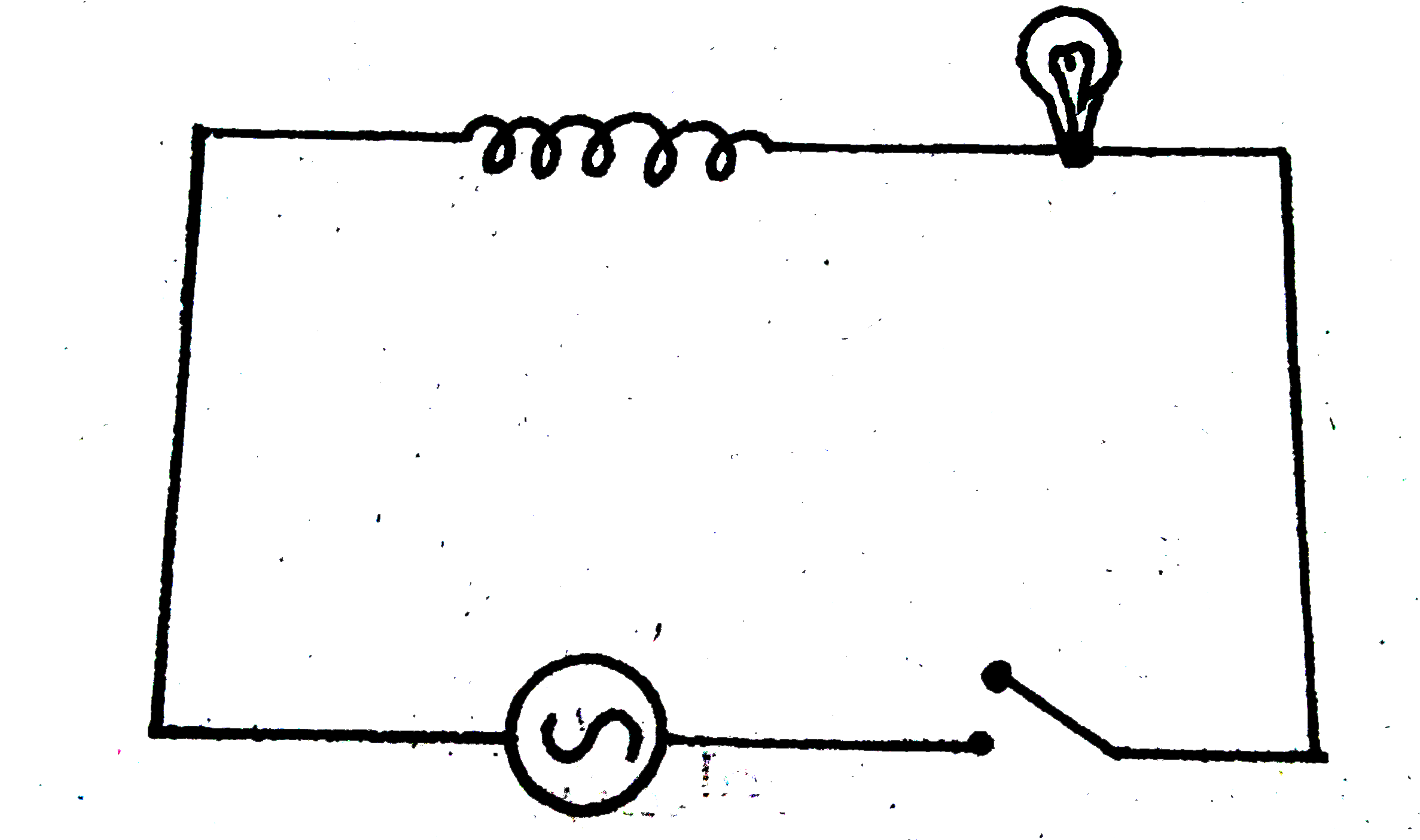Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A light bulb and an open coil inductor are connected to an ac source t...
Text Solution
|
- A light bulb and an open coil inductor are connected to an ac source t...
Text Solution
|
- एक प्रकाश बल्ब और एक सरल प्रेरक कुण्डली एक कुंजी सहित निम्न चित्र।नुस...
Text Solution
|
- A light bulb and an open coil inductor are connected to an ac source t...
Text Solution
|
- एक वायु-क्रोड कुण्डली एवं एक विद्धुत बल्ब एक प्रत्यावर्ती धारा स्रोत क...
Text Solution
|
- An electric bulb is connected in series with an inductor and an Ac sou...
Text Solution
|
- A light bulb and an inductor coil are connected to an ac source throug...
Text Solution
|
- A light bulb and an open coil inductor are connected to an ac source t...
Text Solution
|
- A light bulb and an open coil inductor are connected to an ac source t...
Text Solution
|