Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
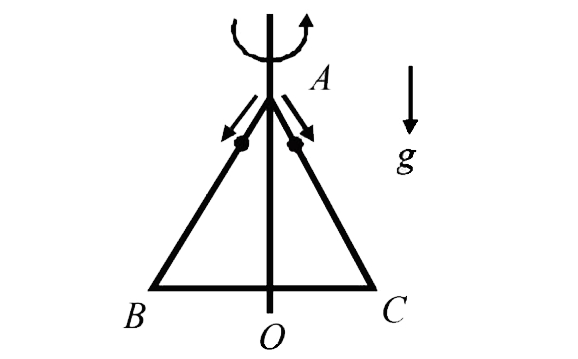
- An equailaral triangle ABC formed from a uniform wire has two small id...
Text Solution
|
- A wire, which passes through the hole in a small bead, is bent in the ...
Text Solution
|
- An equailaral triangle ABC formed from a uniform wire has two small id...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical beads, each of m=100g , are connected by an inextensible...
Text Solution
|
- A equilaterial triangle ABC formed from a uniform wire has two small i...
Text Solution
|
- A bead of mass m is located on a parabolic wire with its axis vertical...
Text Solution
|
- A massless ring hangs from a thread and two beads of mass m slide it w...
Text Solution
|
- एक सर्वत्रसम तार द्वारा बनाए गए समबाहु त्रिभुज के बिंदु A पर दो समरूप ...
Text Solution
|
- Two beads are released from A simultaneoulsy to slide along smooth AB ...
Text Solution
|