Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
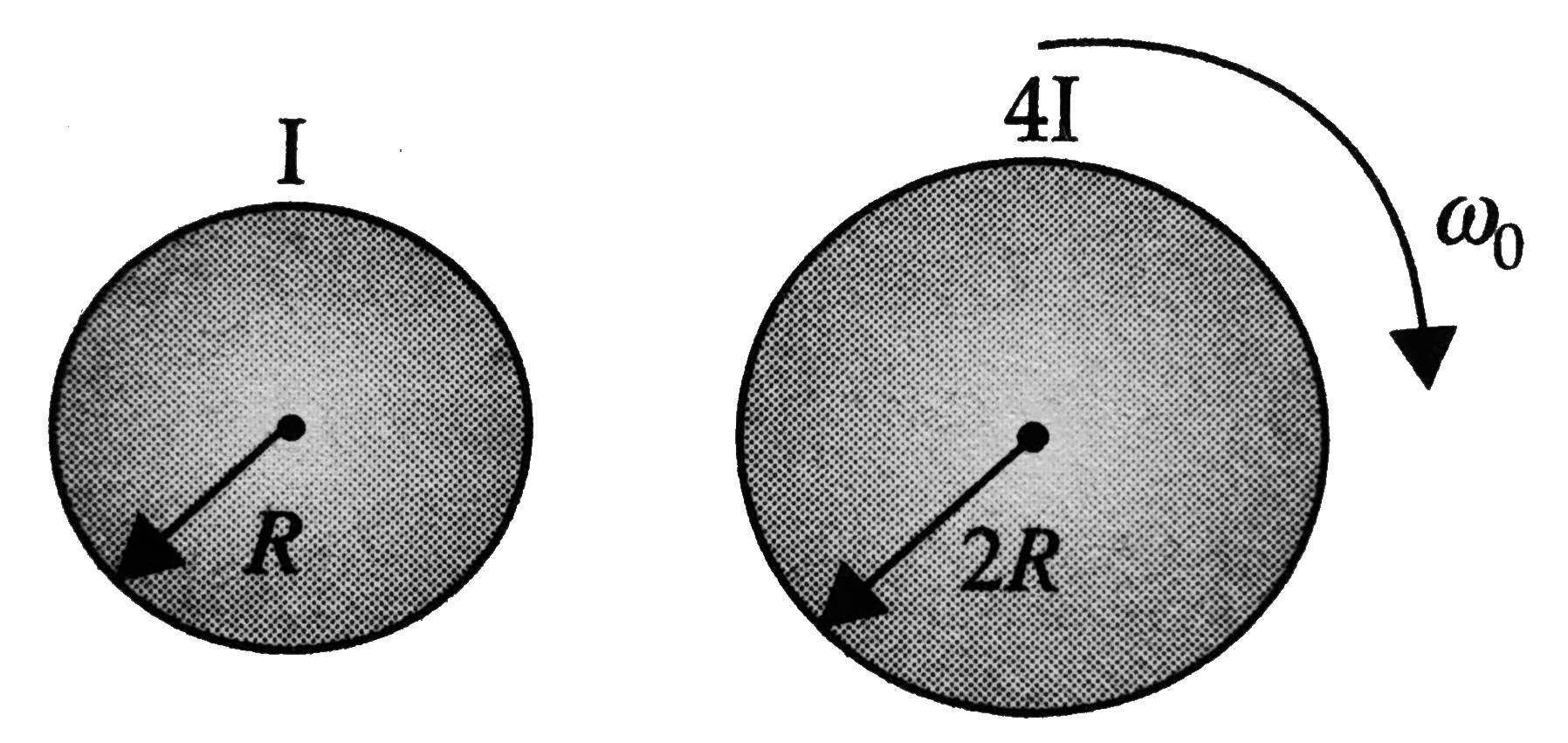
- Two cylinders having radii 2R and R and moment of inertia 4I and I abo...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows two cylinders of raddi r1 and r2 having moments of inerti...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cylinder of radius R is spinned about it axis to the angular...
Text Solution
|
- Two cylinders having radii 2R and R and moment of inertia 4I and I abo...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure the plank resting on two cylinders is horizontal. The pl...
Text Solution
|
- The axis of the uniform cylinder in figure is fixed. The cylinder is i...
Text Solution
|
- The axis of the uniform cylinder in figure is fixed. The cylinder is i...
Text Solution
|
- The axis of the uniform cylinder in figure is fixed. The cylinder is i...
Text Solution
|
- Two cylinders with radii r(1) and r(2) and rotational inertia I(1) and...
Text Solution
|