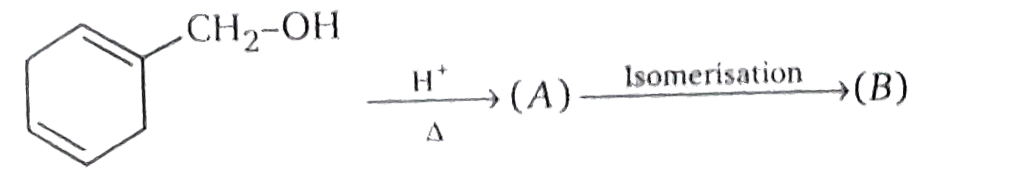Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- (A) on heating isomerizes to (B) .what is the structure of (B) ?
Text Solution
|
- (A) on heating isomerizes to (B) .what is the structure of (B) ?
Text Solution
|
- What type os structural isomerism is shown by alkanes?
Text Solution
|
- What type of structural isomerism is shown by
Text Solution
|
- Isomerism and its types | Structural Isomerism
Text Solution
|
- Structural differences are main in the following isomers (A) ionisat...
Text Solution
|
- Structural differences are main in the following isomers (A) ionisat...
Text Solution
|
- b) What type of structural, isomerism is exhibited by the complex Co (...
Text Solution
|
- What is structural isomerism ? Give two isomers of chain isomerism of ...
Text Solution
|