Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A conducting rod PQ of mass m and length l is placed on two long paral...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod of length l slides at constant velocity v on two para...
Text Solution
|
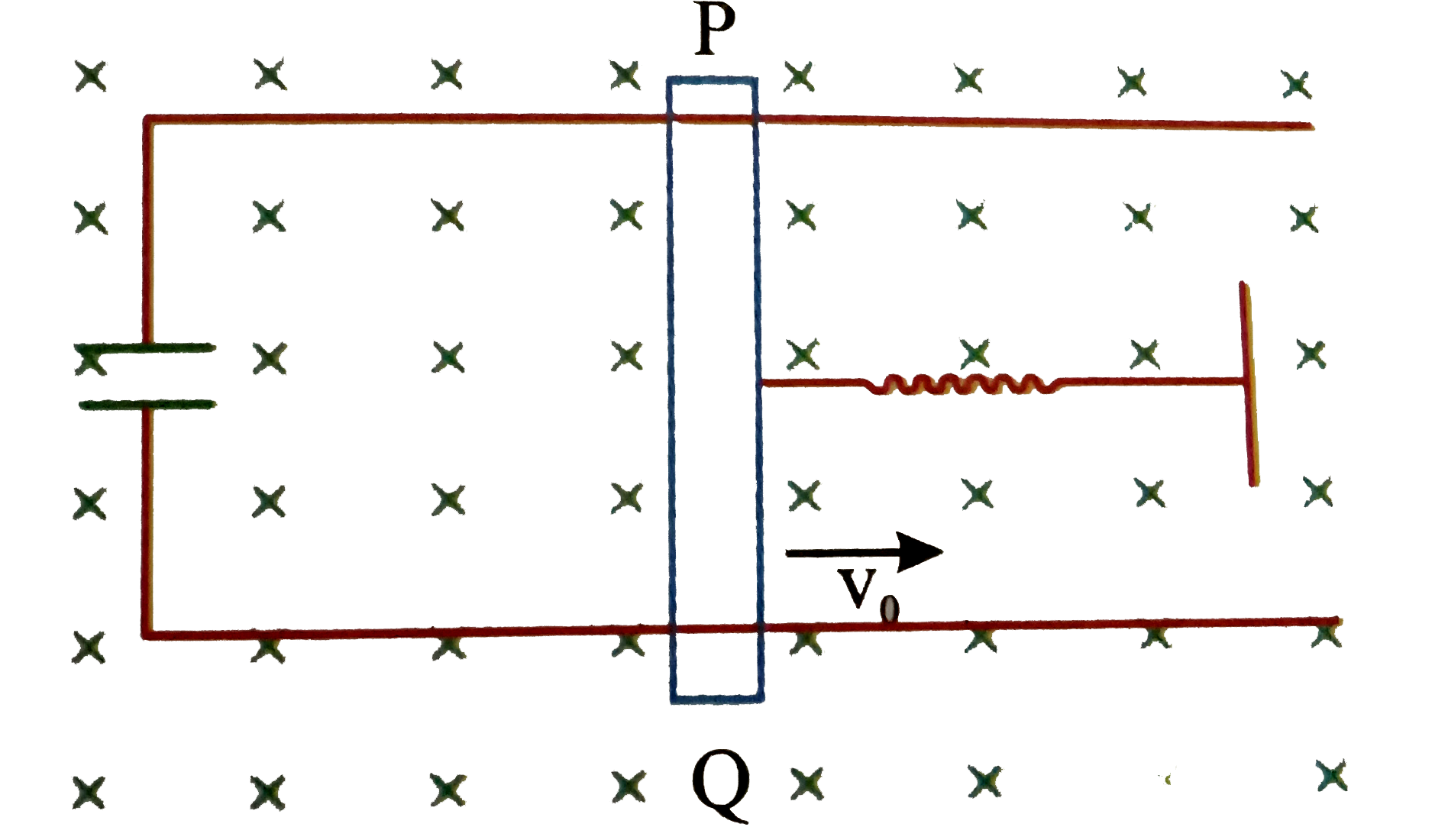
- A conducting rod of length is moved at constant velocity v(0) on two p...
Text Solution
|
- AB and CD are fixed conducting smooth rails placed in a vertical palne...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod PQ of mass m and length l is placed on two long paral...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod MN of mass m and length 'l' is placed on parallel smo...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth horizontal parallel conducting rails are connected with a c...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel fixed conducting rails are l distance apart. They are con...
Text Solution
|
- A pair of long, smooth, parallel, horizontal, conducting rails are joi...
Text Solution
|