Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RIGID BODY DYNAMICS - I
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (SINGLE CORRECT CHOICE TYPE)|43 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS - I
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (MORE THAN ONE CORRECT CHOICE TYPE)|7 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS - I
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise CHECKPOINT|18 VideosRELATIVITY
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)|5 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS-II
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY-RIGID BODY DYNAMICS - I-PROBLEMS
- The flywheel of a steam engine runs with a constant angular velocity o...
Text Solution
|
- A seed is on a turntable rotating at 331/3 rev/min, 6.0 cm from the ro...
Text Solution
|
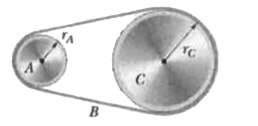
- In Fig. 10-54, wheel A of radius r(A)=10cm is coupled by belt B to whe...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 10-55 shows an early method of measuring the speed of light tha...
Text Solution
|
- A disk, with a radius of 0.25 m, is to be rotated like a merry-go-roun...
Text Solution
|
- A car starts from rest and moves around a circular track of radius 32....
Text Solution
|
- (a) A uniform 2.00 kg disk of radius 0.300 m can rotate around its cen...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 10-56 gives angular speed versus time for a thin rod that rotat...
Text Solution
|
- A meter stick of negligible mass can rotate about a vertical axis thro...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 10-57 a shows a disk that can rotate about an axis at a radial ...
Text Solution
|
- A 0.50 kg meter stick can rotate around an axis perpendicular to the s...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 10-58 shows three 0.0100 kg particles that have been glued to a...
Text Solution
|
- A wheel with a rotational inertia of 0.50kg*m^(2) about its central ax...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 10-59 shows an arrangement of 15 identical disks that have been...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 10-60, two particles, each with mass m = 0.85 kg, are fastened...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 10-61 is an overhead view of a rod of length 1.0 m and mass 1.0...
Text Solution
|
- The uniform solid block in Fig. 10-62 has mass 0.172 kg and edge lengt...
Text Solution
|
- Four identical particles of mass 0.75 kg each are placed at the vertic...
Text Solution
|
- The body shown in Fig. is pivoted at point O. Three forces act on it F...
Text Solution
|
- A 60 kg father and 20 kg child sit on opposite ends of a seesaw consis...
Text Solution
|