Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RIGID BODY DYNAMICS - I
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (SINGLE CORRECT CHOICE TYPE)|43 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS - I
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (MORE THAN ONE CORRECT CHOICE TYPE)|7 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS - I
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise CHECKPOINT|18 VideosRELATIVITY
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)|5 VideosRIGID BODY DYNAMICS-II
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY-RIGID BODY DYNAMICS - I-PROBLEMS
- Force vecF=(2.0N)hati-(3.0N)hatk acts on a pebble with position vector...
Text Solution
|
- A force vecF=(6.00hati-4.00hatj)N acts on a particle with position vec...
Text Solution
|
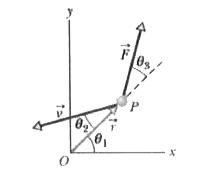
- At the instant of Figure, a 2.0 kg particle P has a position vector ve...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is shot from ground level at initial speed u and ...
Text Solution
|
- A 3.0 kg particle-like object moves in a plane with velocity component...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles each of mass m and speed v, travel in opposite direction...
Text Solution
|
- At the instant the displacement of a 1.50 kg object relative to the or...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 10-72, a 0.400 kg ball is shot directly upward at initial spee...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is acted on by two torques about the origin: vectau(1) has ...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 10-73, a particle of mass m is released from rest at point A, ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 10-74 is an overhead view of a rod of length d and negligible m...
Text Solution
|
- A force (2.00hati-4.00hatj+2.00hatk)N acts on a particle located at (3...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 10-75 shows three rotating, uniform disks that are coupled by b...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, three particles of mass m = 23 g are fastened to three rods...
Text Solution
|
- A sanding disk with rotational inertia 8.6xx10^(-3)kg*m^(2) is attache...
Text Solution
|
- The angular momentum of a flywheel having a rotational inertia of 0.14...
Text Solution
|
- A disk with a rotational inertia of 7.00kg*m^(2) rotates like a merry-...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 10-77 shows a rigid structure consisting of a circular hoop of ...
Text Solution
|
- In Fig. 10-78, two skaters, each of mass 50 kg, approach each other al...
Text Solution
|
- A cockroach of mass 0.20 kg runs counterclockwise around the rim of a ...
Text Solution
|