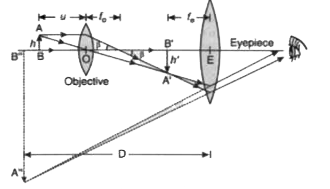
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC-3(LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS)|5 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC-3(Numerical Problems)|3 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC-3(SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS-I)|6 VideosNUCLEI
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise TOPIC -2 (Numerical Problems)|3 VideosSample Paper 1
OSWAAL PUBLICATION|Exercise Exercise|36 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems