Topper's Solved these Questions
PROBABILITY
NCERT BANGLISH|Exercise Optional Exercise|4 VideosPROBABILITY
NCERT BANGLISH|Exercise DO THIS|14 VideosPROBABILITY
NCERT BANGLISH|Exercise Exercise- 13.1|16 VideosPOLYNOMIALS
NCERT BANGLISH|Exercise OPTIONAL EXERCISE [For extensive learning]|6 VideosPROGRESSIONS
NCERT BANGLISH|Exercise OPTIONAL EXERCISE (FOR EXTENSIVE LEARNING)|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT BANGLISH-PROBABILITY-Exercise- 13.2
- A bag contains 3 red balls and 5 black balls. A ball is selected at ra...
Text Solution
|
- A box contains 5 red marbles, 8 white marbles and 4 green marbles. One...
Text Solution
|
- A Kiddy bank contains hundred 50p coins, fifty ₹1 coins, twenty ₹2 coi...
Text Solution
|
- Gopi buys a fish from a shop for his aquarium. The shopkeeper takes ou...
Text Solution
|
- A game of chance consists of spinning an arrow which comes to rest poi...
Text Solution
|
- One card is selected from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the p...
Text Solution
|
- Five cards-the ten, jack, queen, king and ace of diamonds, are well-sh...
Text Solution
|
- 12 defective pens are accidentally mixed with 132 good ones. It is not...
Text Solution
|
- A lot of 20 bulbs contain 4 defective ones. One bulb is selected at ra...
Text Solution
|
- A box contains 90 discs which are numbered from 1 to 90. If one disc i...
Text Solution
|
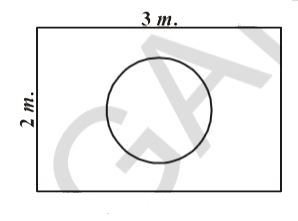
- Suppose you drop a die at random on the rectangular region shown in fi...
Text Solution
|
- A lot consists of 144 ball pens of which 20 are defective and the othe...
Text Solution
|
- Two dice are rolled simultaneously and counts are added (i) complete t...
Text Solution
|
- А game consists of tossing a one rupee coin 3 times and noting its out...
Text Solution
|
- A dice is thrown twice. What is the probability that (i) 5 will not co...
Text Solution
|