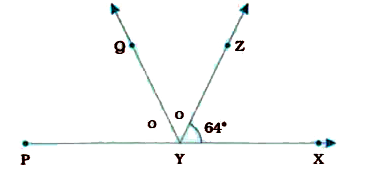Topper's Solved these Questions
LINES AND ANGLES
NCERT GUJARATI|Exercise EXERCISE XERCISE - 4.3|19 VideosLINES AND ANGLES
NCERT GUJARATI|Exercise EXERCISE XERCISE - 4.4|17 VideosLINES AND ANGLES
NCERT GUJARATI|Exercise EXERCISE XERCISE - 4.1|11 VideosLINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
NCERT GUJARATI|Exercise EXERCISE 8.5|1 VideosPOLYNOMIALS AND FACTORISATION
NCERT GUJARATI|Exercise TRY THESE|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT GUJARATI-LINES AND ANGLES -EXERCISE XERCISE - 4.2
- In the given figure three lines bar(AB) , bar(CD) and bar(EF) intersec...
Text Solution
|
- Find the value of x in the following figures.
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure lines bar(AB) and bar(CD ) intersect at O. If angl...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure lines bar(XY) and bar(MN) intersect at O. If ∠PO...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure anglePQR = anglePRQ, then prove that anglePQS = a...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, if x + y = w + z, then prove that AOB is a line.
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure bar(PQ) is a line. Ray bar(OR) is perpendicular t...
Text Solution
|
- It is given that angleXYZ=64^(@) and XY is produced to point P. Draw a...
Text Solution
|