Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT GUJARATI-PROBABILITY -DO THIS
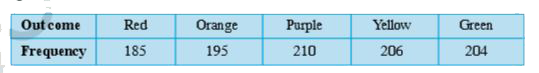
- A spinner was spun 1000 times and the frequency of outcomes was record...
Text Solution
|
- Toss a coin for number of times as shown in the table. And record your...
Text Solution
|
- If three coins are tossed simultaneously then write their outcomes. ...
Text Solution
|
- Classify the following statements into the categories less likely, eq...
Text Solution
|