Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT GUJARATI-TRIGONOMETRY -Do THIS
- Write length of "Hypotenuse ","Opposite side "and "Adjacent side "for ...
Text Solution
|
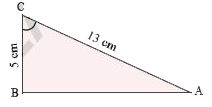
- Find (i) sin C (ii) cos C and (iii) tan C in the adjacent triangle.
Text Solution
|
- In triangle XYZ, angle Y is right angle , XZ =17cm and YZ =15 cm then ...
Text Solution
|
- In a triangle PQR with right angle at Q , the value of ∠P is x , PQ =...
Text Solution
|
- Find the values of cosec 60 ^(@) ,sec 60^(@) and cot 60^(@)
Text Solution
|
- If sin C =( 15)/(17) , then find cos C ,
Text Solution
|
- If tan x = ( 5)/( 12), then find sec x.
Text Solution
|
- If cosec theta =(25)/( 7), then find cot theta
Text Solution
|