An analysis of monthly wages paid to workers in two firms A and B , belonging to the same industry , gives the following results:
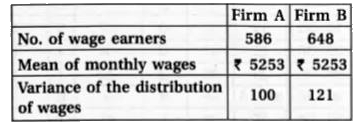
(i) Which firm A or B pays larger amount as monthly wages?
(ii) Which firm , A or B, shows greater variability in individual wages?
An analysis of monthly wages paid to workers in two firms A and B , belonging to the same industry , gives the following results:

(i) Which firm A or B pays larger amount as monthly wages?
(ii) Which firm , A or B, shows greater variability in individual wages?

(i) Which firm A or B pays larger amount as monthly wages?
(ii) Which firm , A or B, shows greater variability in individual wages?
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
(i) B, (ii) B
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Two plant A and B of a factory show following results about the number of workers and the wages paid to them. In which plant, A or B is there greater variability in individual wages ?
An analysis of monthly wagis paid to worker in two parts. A anb B of factory are given below: Which part A or B, show greater variability in indiviual wages?
Two farmers Ramkishan and Gurpreet singh cultivates only three varieties of rice namely Basmati , perimal and Jirasar .The sales (in Rs.) of these varieties of rice by both the farmers in the months of September October are given by the following matrices A and B. (i) Find the combined sales in September and October for each farmer in each variety. (ii) In which month the selling is maximum.
Study the circuits (a) and (b) shown in figure and answer the following questions. (a) Under which conditions would the rms currents in the two circuits be the same ? (b) Can the rms current in circuit (b) be larger than that in (a) ?
Figure shows the velocity-time graph for two masses R and S that collided elastically. Which of the following statements is true? i. R and S moved in the same direction after the collision. ii. The velocities of R and S were equal at the mid time of the collision. iii. The mass of R was greater than mass of S . Which of the following is true?
One urn contains two black balls (labelled B_(1) and B_(2) ) and one white ball. A second urn contains one black ball and two white balls (labelled W_(1) , and W_(2) ). Suppose the following experiment is performed. One of the two urns is chosen at random. Next a ball is randomly chosen from the urn. Then a second ball is chosen at random from the same urn without replacing the first ball. (i) Write the sample space showing all possible outcomes (ii) What is the probability that two black balls are chosen ? (iii) What is the probability that two balls of opposite colour are chosen ?
Two elements M and N belong to the same period of the modern periodic table and are in group I and group II respectively. Compare their following properties : Atomic size (b) Metallic character ( c) Valency of oxides (d) Molecular formula of their chlorides
Thin films, including soap bubbles and oil show patterns of alternative dark and bright regions resulting from interference among the reflected ligth waves. If two waves are in phase, their crests and troughs will coincide. The interference will be cosntructive and the amlitude of resultant wave will be greater then either of constituent waves. If the two wave are not of phase by half a wavelength (180^(@)) , the crests of one wave will coincide width the troughs of the other wave. The interference will be destructive and the ampliutde of the resultant wave will be less than that of either consituent wave. 1. When incident light I, reaches the surface at point a, some of the ligth is reflected as ray R_(a) and some is refracted following the path ab to the back of the film. 2. At point b, some of the light is refracted out of the film and part is reflected back through the film along path bc. At point c, some of the light is reflected back into the film and part is reflected out of the film as ray R_(c) . R_(a) and R_(c) are parallel. However, R_(c) has travelled the extra distance within the film fo abc. If the angle of incidence is small, then abc is approxmately twice the film's thickness . If R_(a) and R_(c) are in phase, they will undergo constructive interference and the region ac will be bright. If R_(a) and R_(c) are out of phase, they will undergo destructive interference and the region ac will be dark. I. Refraction at an interface never changes the phase of the wave. II. For reflection at the interfere between two media 1 and 2, if n_(1) gt n_(2) , the reflected wave will change phase. If n_(1) lt n_(2) , the reflected wave will not undergo a phase change. For reference, n_(air) = 1.00 . III. If the waves are in phase after reflection at all intensities, then the effects of path length in the film are: Constrictive interference occurs when 2 t = m lambda // n, m = 0, 1,2,3 ,... Destrcutive interference occurs when 2 t = (m + (1)/(2)) (lambda)/(n) , m = 0, 1, 2, 3 ,... If the waves are 180^(@) out of the phase after reflection at all interference, then the effects of path length in the film ara: Constructive interference occurs when 2 t = (m + (1)/(2)) (lambda)/(n), m = 0, 1, 2, 3 ,... Destructive interference occurs when 2 t = (m lambda)/(n) , m = 0, 1, 2, 3 ,... A thin film with index of refraction 1.33 coats a glass lens with index of refraction 1.50. Which of the following choices is the smallest film thickness that will not reflect light with wavelength 640 nm?
Thin films, including soap bubbles and oil show patterns of alternative dark and bright regions resulting from interference among the reflected light waves. If two waves are in phase, their crests and troughs will coincide. The interference will be constructive and the amplitude of resultant wave will be greater then either of constituent waves. If the two wave are not of phase by half a wavelength (180^(@)) , the crests of one wave will coincide width the troughs of the other wave. The interference will be destructive and the amplitude of the resultant wave will be less than that of either constiuent wave. 1. When incident light I, reaches the surface at point a, some of the light is reflected as ray R_(a) and some is refracted following the path ab to the back of the film. 2. At point b, some of the light is refracted out of the film and part is reflected back through the film along path bc. At point c, some of the light is reflected back into the film and part is reflected out of the film as ray R_(c) . R_(a) and R_(c) are parallel. However, R_(c) has traveled the extra distance within the film of abc. If the angle of incidence is small, then abc is approximately twice the film's thickness . If R_(a) and R_(c) are in phase, they will undergo constructive interference and the region ac will be bright. If R_(a) and R_(c) are out of phase, they will undergo destructive interference and the region ac will be dark. I. Refraction at an interface never changes the phase of the wave. II. For reflection at the interfere between two media 1 and 2, if n_(1) gt n_(2) , the reflected wave will change phase. If n_(1) lt n_(2) , the reflected wave will not undergo a phase change. For reference, n_(air) = 1.00 . III. If the waves are in phase after reflection at all intensities, then the effects of path length in the film are: Constrictive interference occurs when 2 t = m lambda // n, m = 0, 1,2,3 ,... Destructive interference occurs when 2 t = (m + (1)/(2)) (lambda)/(n) , m = 0, 1, 2, 3 ,... If the waves are 180^(@) out of the phase after reflection at all interference, then the effects of path length in the film area: Constructive interference occurs when 2 t = (m + (1)/(2)) (lambda)/(n), m = 0, 1, 2, 3 ,... Destructive interference occurs when 2 t = (m lambda)/(n) , m = 0, 1, 2, 3 ,... 72. A film with index of refraction 1.50 coats a glass lens with index of refraction 1.80. What is the minimum thickness of the thin film that will strongly reflect light with wavelength 600 nm?