Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT GUJARATI-KINETIC THEORY-EXERCISES
- Estimate the fraction of molecular volume to the actual volume occupie...
Text Solution
|
- Molar volume is the volume occupied by 1 mol of any (ideal) gas at sta...
Text Solution
|
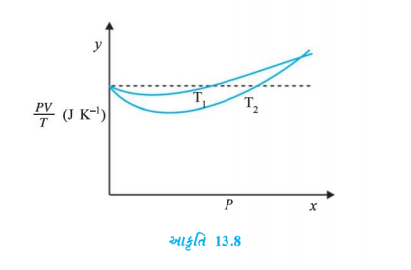
- Figure Show plot of PV//T versus P for 1.00xx10^(-3) kg of oxygen gas ...
Text Solution
|
- An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litres has an initial gauge pressure o...
Text Solution
|
- An air bubble of volume 1.0 cm^(3) rises from the bottom of a lake 40 ...
Text Solution
|
- Estimate the total number of air molecules (inclusive of oxygen, nitro...
Text Solution
|
- Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at (i) room tempe...
Text Solution
|
- Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and...
Text Solution
|
- At what temperature is the root mean square speed of an atom in an arg...
Text Solution
|
- Estimate the mean free path and collision frequency of a nitrogen mole...
Text Solution
|