Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT GUJARATI-CURRENT ELECTRICITY -ADDITIONAL EXERCISES
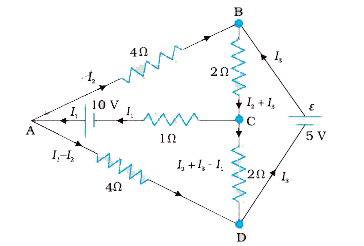
- Determine the current in each brance of the network showin in
Text Solution
|
- The earth's surface has a negative surface charge density of 10^(-9)C ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Six lead-acid type of secondary cells each of emf 2.0 V and intern...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires of equal length, one of aluminium an the other of copper hav...
Text Solution
|
- What conclusion can you draw from the follwing observation on a resist...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following questions: (a) A steady current flows in a meta...
Text Solution
|
- Choose the correct alternative: (a) Alloys of metals usually have (g...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Given n resistores each of resistance R. how will you combine them...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the furrent drawn from a 12 V suly with internal resistacne ...
Text Solution
|
- show a 2.0V potentiometer used for the determination of internal resis...
Text Solution
|