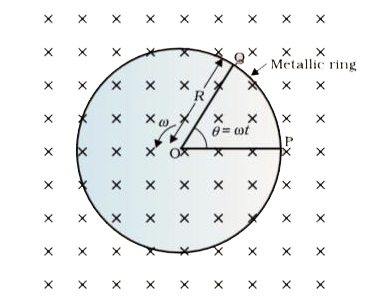
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT GUJARATI-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-ADDITIONAL EXERCISES
- A metallic rod of 1 m length is rotated with a frequency of 50 rev/s, ...
Text Solution
|
- Suppose the loop is stationary but the current feeding the electromagn...
Text Solution
|
- A square loop of side 12 cm with its sides parallel to X and Y axes is...
Text Solution
|
- It is desired to measure the magnitude of field between the poles of a...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a metal rod PQ resting on the smooth rails AB and positio...
Text Solution
|
- An air-cored solenoid with length 30 cm, area of cross-section 25 "cm"...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Obtain an expression for the mutual inductance between a long stra...
Text Solution
|
- A line charge lambda per unit length is lodged uniformly onto the rim ...
Text Solution
|