Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
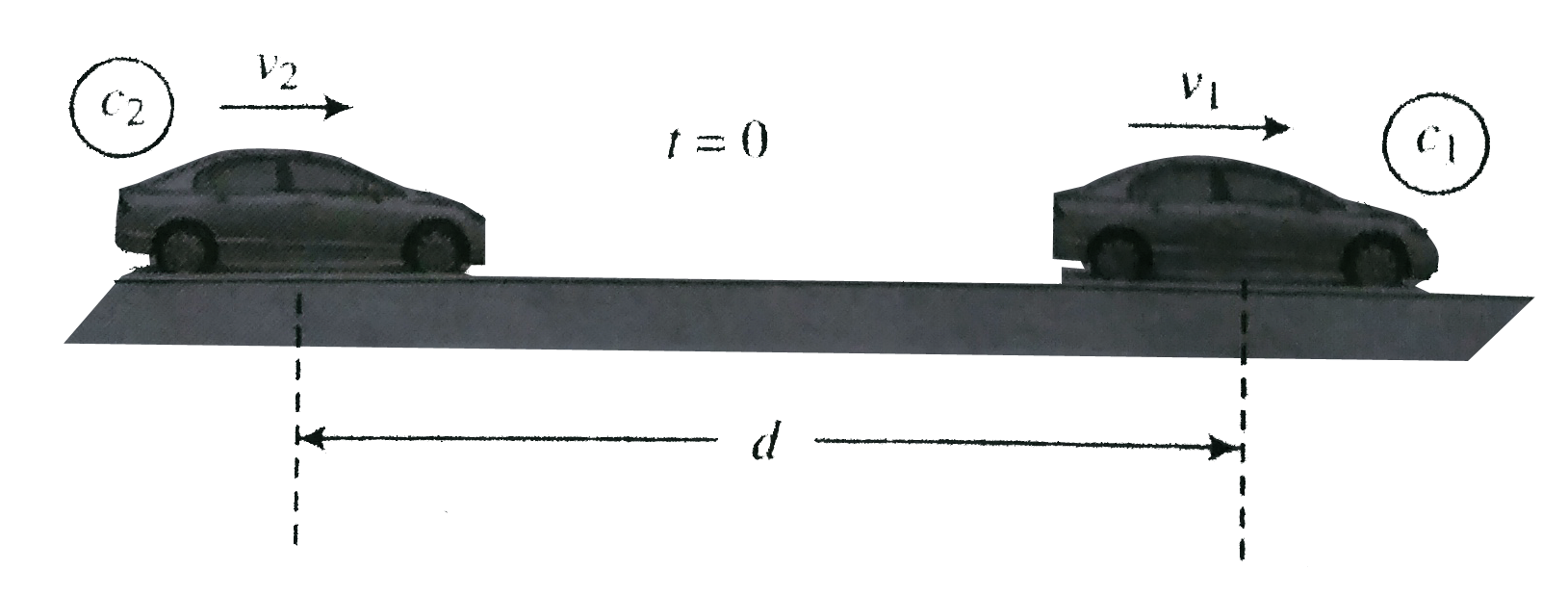
- Two cars C(1) and C(2) moving in the same direction on a straight sing...
Text Solution
|
- Two cars 1 and 2 move with velocities v(1) and v(2), respectively, on ...
Text Solution
|
- Two cars C(1) and C(2) moving in the same direction on a straight sing...
Text Solution
|
- The capacities of two parallel plate capacitors are C(1) and C(2) and ...
Text Solution
|
- Two cars C(1) and C(2) are moving on parallel roads in the same direct...
Text Solution
|
- A car C(1) travelling at a uniform speed of 75 kph passed another C(2...
Text Solution
|
- The value of the determinant |(1,1,1),(.^(m)C(1),.^(m +1)C(1),.^(m+2)C...
Text Solution
|
- सारणिक |(1,1,1),(.^(m)C(1),.^(m+1)C(1),.^(m+2)C(1)),(.^(m)C(2),.^(m+1)...
Text Solution
|
- सिद्ध कीजिए कि : |(1,1,1),(""^(m)C(1),""^(m+1)C(1),""^(m+2)C(1)),...
Text Solution
|
 .
.