Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
XII BOARDS PREVIOUS YEAR-XII BOARDS-SET-I
- Two nuclei have mass number in the ratio 1:8. What is the ratio of the...
Text Solution
|
- Give the logic symbol of NOR gate.
Text Solution
|
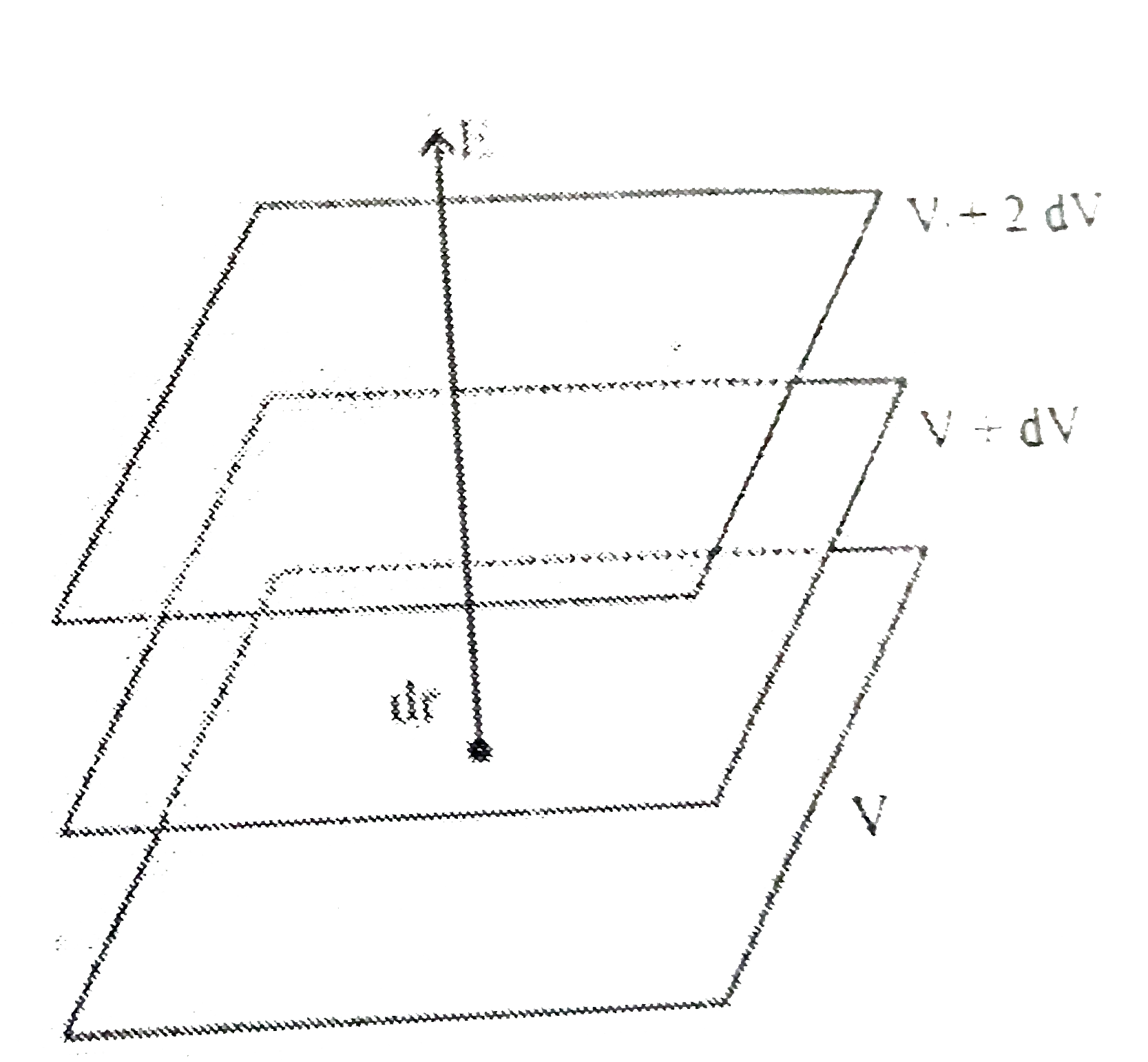
- Draw 3 equipotential surfaces corresponding to a field that uniforml...
Text Solution
|
- Define electric flux. Write its SI unit. A charge q is enclosed by a s...
Text Solution
|
- Define refractive index of a transparent medium. A ray of light passes...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the current the current drawn from the battery by the networ...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following questions : (a) Optical and radio telescopes ar...
Text Solution
|
- How does the resistivity of a consuctor depend upon temperature electr...
Text Solution
|
- Define the term 'linearly polarised light'. When does the intensity ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of 15 Omega resistance is gradually stretched to double in orig...
Text Solution
|
- (a) The mass of a nucleus in its ground state is always less than tota...
Text Solution
|
- Write the function of (i) Transducer and (ii) Repeater in the context ...
Text Solution
|
- Write two factors justifying the need of modulation for transmission o...
Text Solution
|
- A positive point charge (+q) is kept in the vicinity of an uncharged c...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery. After some time th...
Text Solution
|
- (i) State the principle of working of a meter bridge. (ii) In a mete...
Text Solution
|
- (i) State Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. (ii) A jet pla...
Text Solution
|
- Laser light of wavelength 630 nm incident on a pair of slits produces ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a schematic arrangement of the Geiger Marsden experiment. How did...
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between sky wave and space wave propagation. Give a brief ...
Text Solution
|