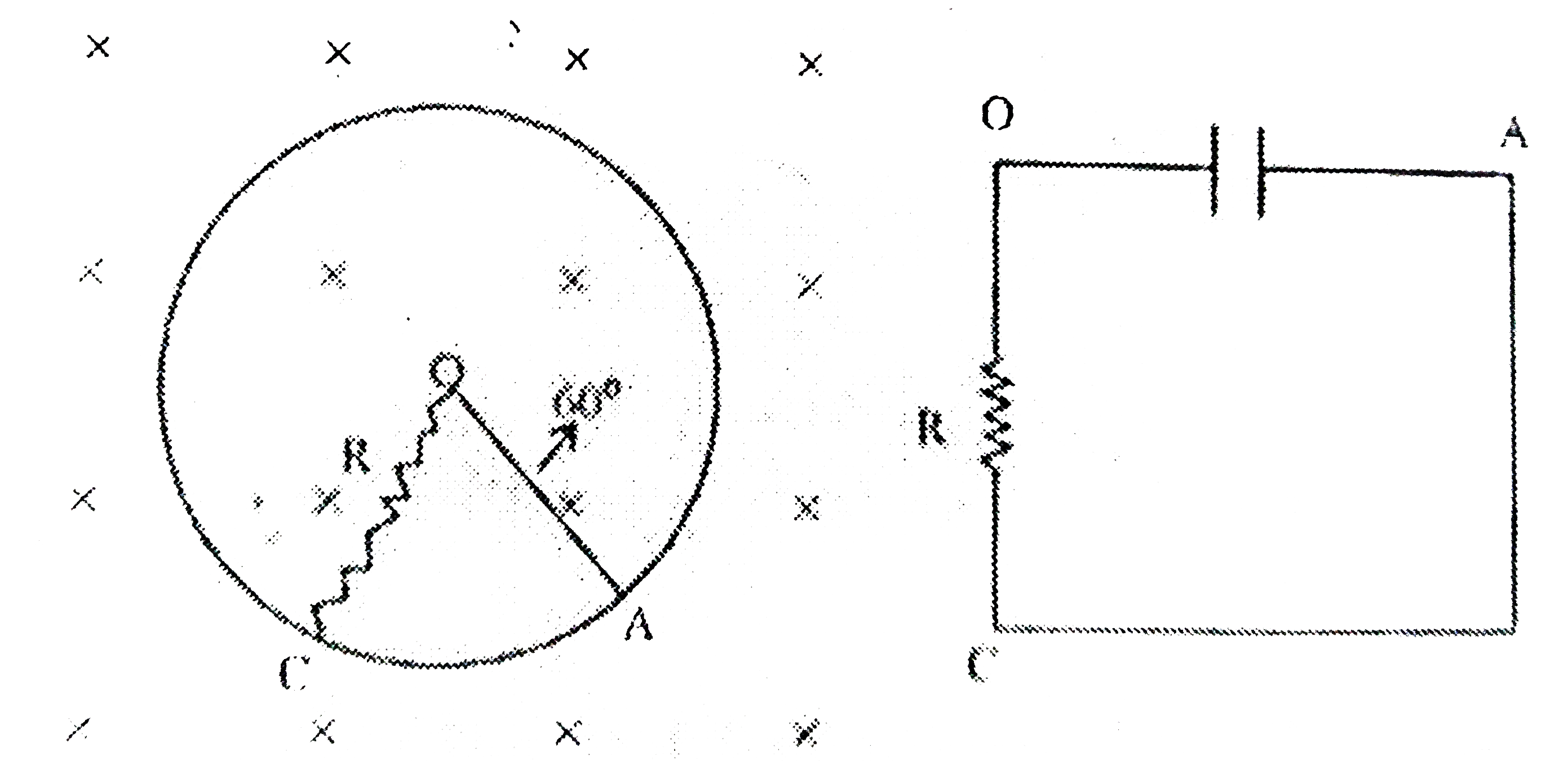Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A metallic rod of 'L' length is rotated with angular frequency of 'w' ...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of 1 m length is rotated with a frequency of 50 rev//s,...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of length 'I' is rotated with a frequency with one end ...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of 'L' length is rotated with angular frequency of 'w' ...
Text Solution
|
- A metallie rod of 1 m length is rotated with a frequency of 50 revis, ...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of 1m length is rotated with a frequency of 50 rev/s, w...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of 1 m length is rotated with a frequency of 50 rev/s, ...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of 1 m length is rotated with a frequency of 50 rev/s, ...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic rod of 'L' length is rotated with angular frequency of 'w' ...
Text Solution
|