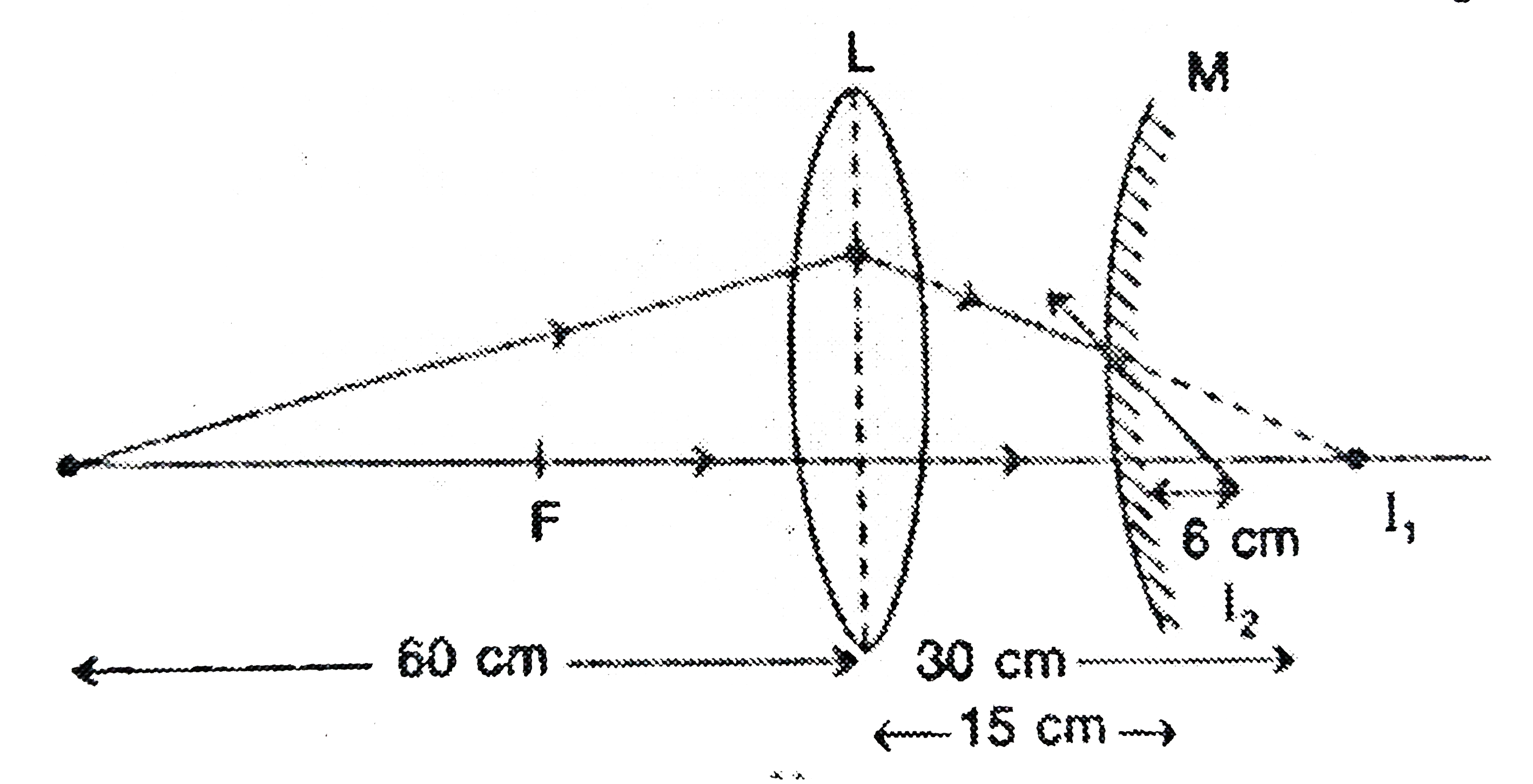Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
XII BOARDS PREVIOUS YEAR-XII BOARDS-SET-I
- Estimate the average drift speed of conduction electrons in a copper w...
Text Solution
|
- Two monochromatic ray of light are incident normally on the face AB of...
Text Solution
|
- Write the function of (i) Transducer and (ii) Repeater in the context ...
Text Solution
|
- Show diagrammatically the behaviour of magnetic field lines in the pre...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Using the phenomenon of polarization, show, how, transverse natur...
Text Solution
|
- Define the term 'mutual inductance' between the two coils. Obtain the...
Text Solution
|
- Answer the following : (a) Why are the connections between the resi...
Text Solution
|
- R Omega का कोई प्रतिरोध एक पोटेंशियोमीटर से विघुत धारा प्राप्त कर रहा...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens of focal length 20 cm is placed co-axially with a convex...
Text Solution
|
- A voltage V = V(0)sinomegat is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive...
Text Solution
|
- Write any two distinguishing features between conductors, semiconducto...
Text Solution
|
- For the past some time, Aarti had been observing some erratic body mov...
Text Solution
|
- Write two basic modes of communication. Explain the process of amplitu...
Text Solution
|
- An electron microscope uses electrons accelerated by a voltage of 50kV...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a labelled diagram of Van de Graff generator. State its working p...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Deduce the expression for the torque acting on a dipole of dipole ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) In Young's double slit experiment, describe briefly how bright and...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Describe briefly how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Deduce an expression for the frequency of revolution of a charged ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Draw a labellel diagram of a moving coil galvanometer. Describe br...
Text Solution
|