(a) `S_(1)P =S_(2)P`
The distances `S_(1)P and S_(2)P` are equal, waves from ` S_(1) and S_(2)` will take the same to travel to the point.
Displacement produced by the sources `S_(1) ` at the point P is given by
` y_(1) = a cos omegat`
The displacement produced by the sources `S_(2)` (at point P) will alos be gibven by
` y_(2)= acos omegat`
Thus, the resultant of displacement at P would be given by
`y= y_(1) +y_(2) = 2 a cos omegat`
The intensity is the poportional to the square of the amplitude, the resultant intensity will be given by
` I= 4a^(2)`
`I_(o)` represent the intensity produced by each of the individual sources.
`I_(o) alpha a^(2)`
In fact at any point on the prependicular bisector of `S_(1) S_(2)` , the intensity will be `4I_(o)` as construct9ive interfernce next point is Q.
` S_(2) Q- S_(1) Q = 2lambda`
` y_(1) =a cos omegat`
if ,
the displacement produced by `S_(2)` will be given by
` y_(2) = a cos ( omegat - 4pi) = a cos omegat`
Next consdier point R :
` S_(2) R-S_(1)R= 2.5 lambda`
` y_(1), = a cos omegat`
` y_(2) = a cos omegat-5lambda`
`= - a cos omegat`
A destructive interference andt eh resultant intensirt will be zero. so other arbitrary point `C_(1)` .
The displacement produced by ` S_(1)` is given by
` y_(1) =n cos omega t`
`y_(2)= a cos (omegat + phi)`
and resultant displacement willl be given by
` y = y_(1) +y_(2)`
`a [ cos omegat+cos (omegat + phi )]`
` 2 a cos (phi/2) cos (omegat + phi/2)`
The amplitude of the resultant displacement is ` 2 a cos (phi/2)` and therefore the intensity at that point will be
` I= 4I_(o) cos^(2) (phi/2)`
` if phi = 0 +- 2pi, +-4 pi` ...., which correspoinds to the condition in costructive interference. Leading to maximum intensity, on the other hand, if
` phi = +- pi, +-3 pi, 5 pi`
which corresponds to the condition have destructive interference leading to zero intensity,
(b) (i) As the width of the slits ix increased, the fringe width decrease. It is beacause,
` beta alpha 1/d`
(ii) The different colours of white light will produce different interence patterns but the central bright friges due to all colours are at teh sme positions, therefore, the central bright fringe is white in colour. since the wavelength of the light is smallest, the fringe closest, on the either side of the central with frige is blue and fasthest is red. Beyond a few fringres, no clear patten is visible.
OR
(a) Let the incident ray meet refracting face AB of the prism at point P. Ray PQ is the refracted ray inside th prism and ` delta_(2) and r_(1)` are the angle of deviation and refraction at interface AB. At interface AC the ray goes out of the prism. Let e be the angle of emergence. The angle of deviation at point Q is ` delta_(2)` as shown in figure.
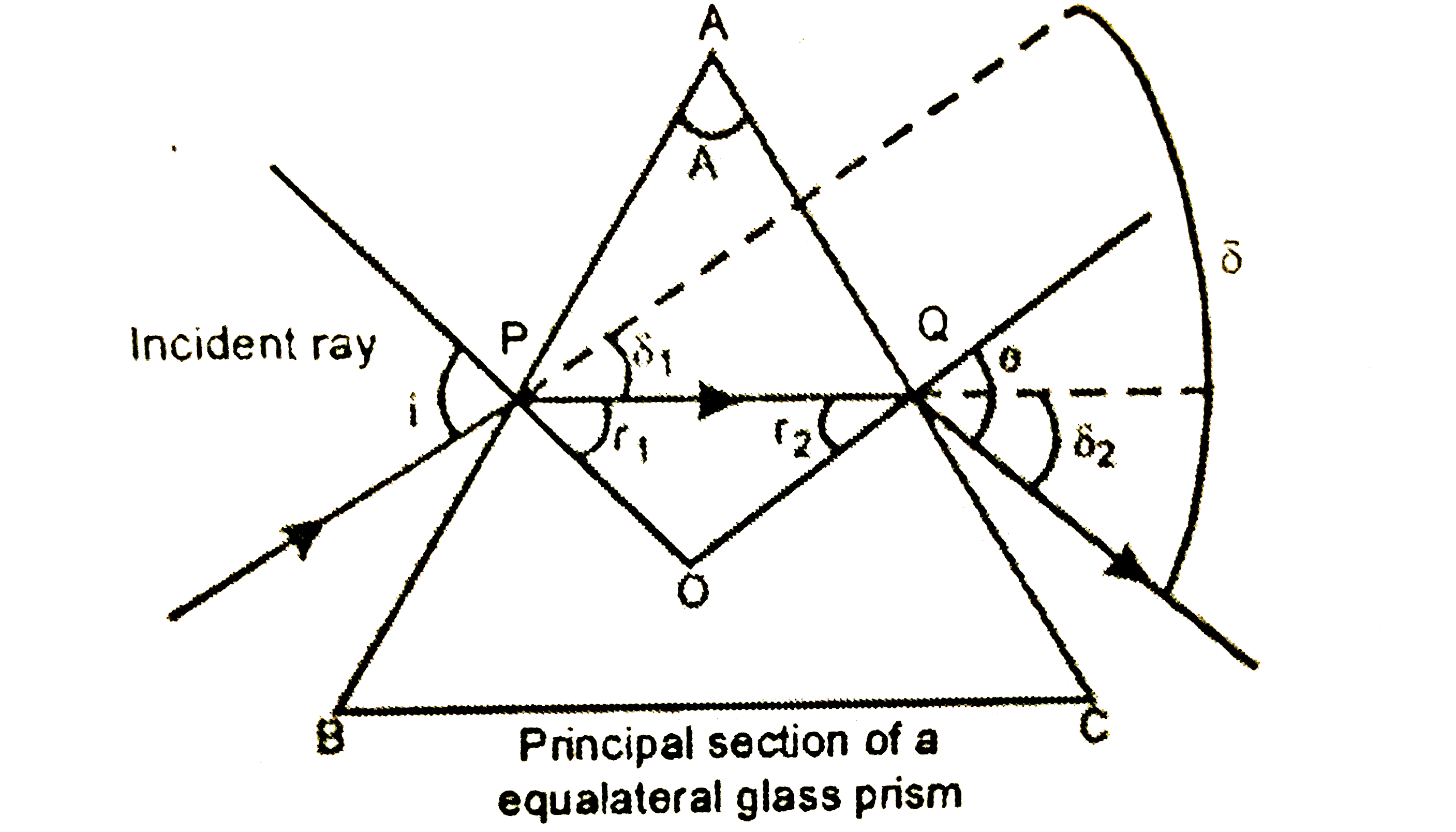
Using geometry, we see that at point P,
` i = delta_(1) +r_(1) " " delta_(1) = i- r_(1)`
and at point Q, ` e = delta_(2) + r_(2)`
`delta_(2) = e-r_(2)`
The total deviation `delta`, suffered by the incident ray is equal to` delta_(1) + delta_(2)`
` delta= delta_(1) + delta_(2)`
` ( i -r_(1))^(2) + ( e -r_(2)) = ( i +e) - (r_(1) +r_(2))`
In quadrilatent POQA, the sum of all four angle is `360^(@)`
` P + O+Q+A = 360^(@)`
as P and Q both are right angles.
` P+Q = 180^(@)`
`O +A = 180^(@)`
In triangle POQ
` O + r_(1)+r_(2) = 180^(@)`
In triangle POQ ,
` O + r_(1) + r_(2) = 180^(@)`
comparing equations (ii) and (iii), we have
` A= r_(1) + r_(2)`
Subsituting this value in equation (i)
` delta= i + e -A`
` delta +A = i +e`
(b) A ray of light incident on face AB will just suffer internal reflection at the other face, AC , if it goes incident on the face AC at an angle equal to the critical angle for the crititcal angle for the material of the prism. If critical angle for the material fo prism is C.
` sin C = 1/ mu = 1/ (1.524) = 0.6562`
` C= 41^(@)`
Now , for a prism,
` r_(1) + r_(2) =A`
` r_(2) = C` we have
` r_(1) +C = A or r_(1)=A -c`
Setting , the values of A and C, we obtain,
` r_(1) = 69^(@) - 41^(@) =1 9^(@)`
At the face, AB : `sini/sinr_(1) =muorsini/(sin19^(@))=1.524`
`sini = 1.524 xx sin19^(@)`
`= 1.524 xx 0.3256 = 0.4962`
` i = 29.75^(@)`
