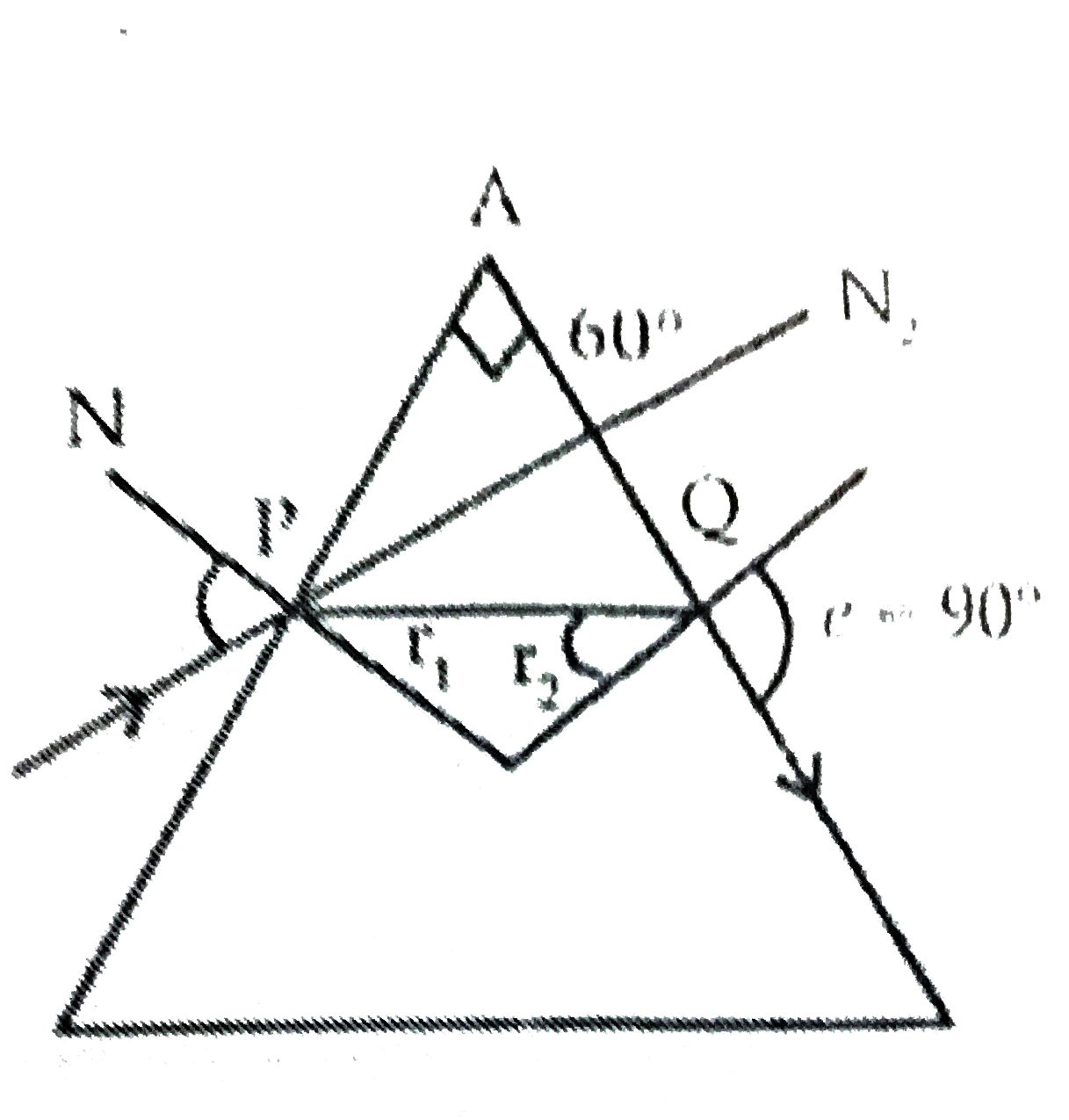
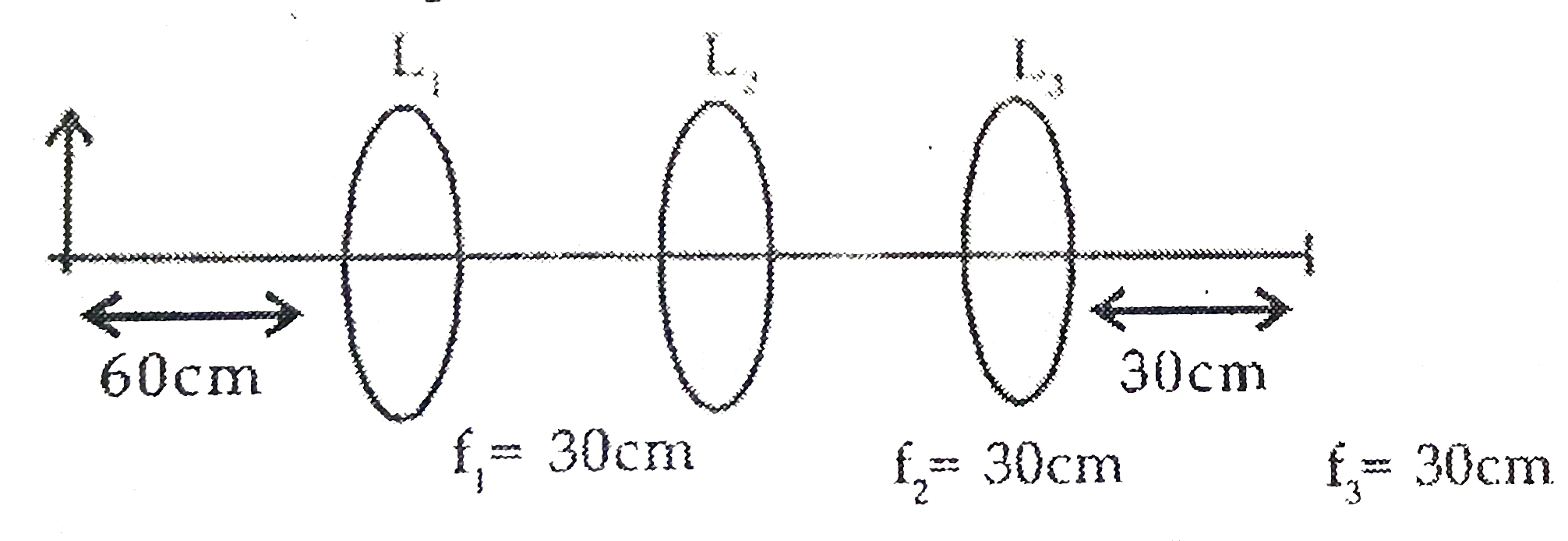Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- (a) Explain with reason, how the power of a diverging lens changes whe...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 7.44 shows three similar lamps L(1) , L(2), and L(3) connectged...
Text Solution
|
- Explain with reason how the power of a diverging lens changes when (...
Text Solution
|
- Three lenses L(1) , L(2) , L(3) are placed co-axially as shown in figu...
Text Solution
|
- You are given three lenses L(1),L(2) and L(3) each of focal length 20 ...
Text Solution
|
- You are given three lenses L(1),L(2) and L(3) each of focal length 10 ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Explain with reason, how the power of a diverging lens changes whe...
Text Solution
|
- तीन उत्तल लेंस L(1), L(2) तथा L(3) एक ही ज्यामितीय आकार के बने हैं । L...
Text Solution
|
- फोकस दुरी 6 सेमी का एक उत्तल लेंस L(1), फोकस दुरी 6 सेमी का एक अवतल ले...
Text Solution
|