Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R is pivoted smoothly at its centr...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass M and radius R is pivoted about the horizontal ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform vertical rod of mass m and length l pivoted at point O ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R is pivoted smoothly at its centr...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m and radius R=(80)/(23pi^2)m is pivoted smooth...
Text Solution
|
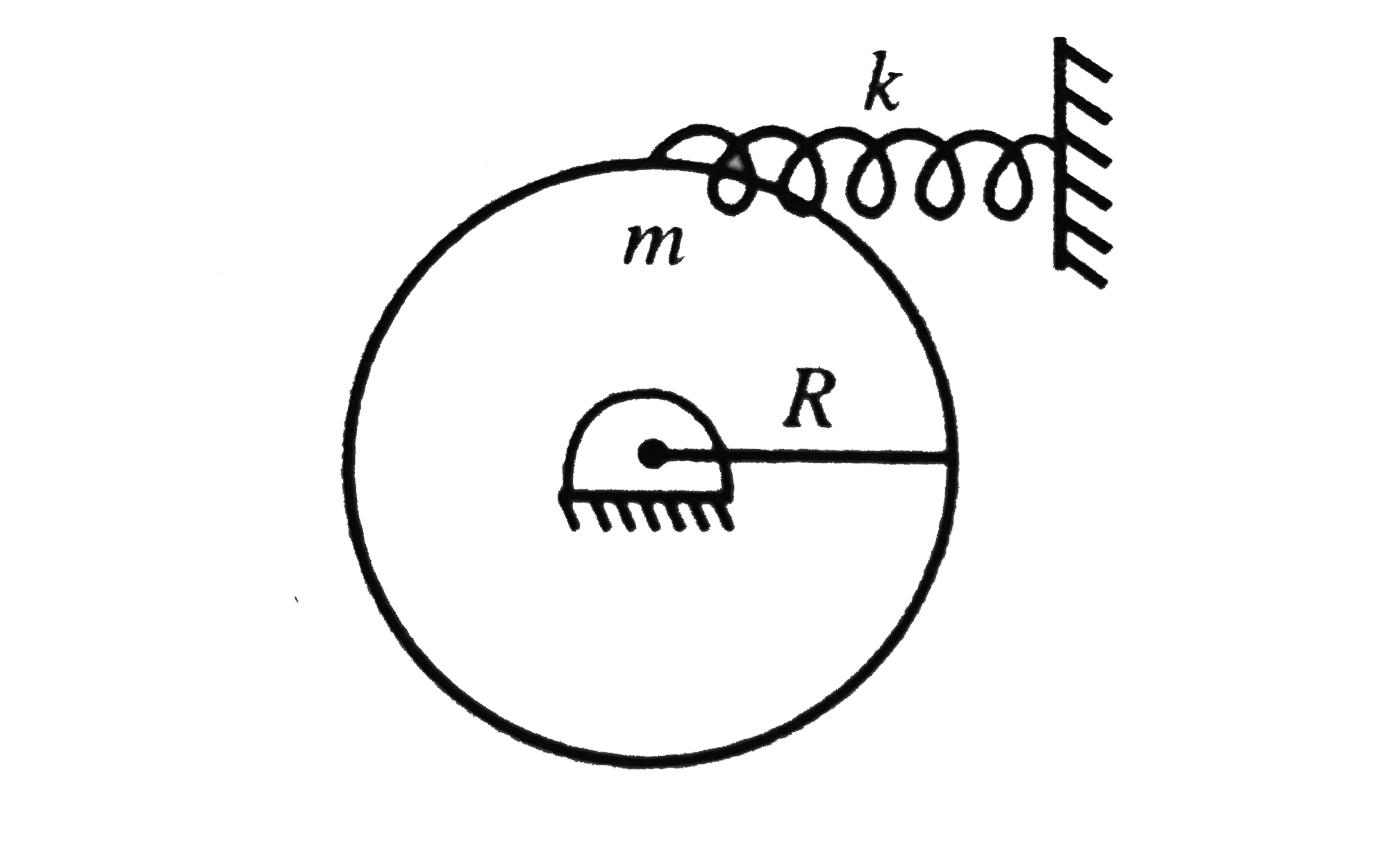
- In the system shown in Fig, a disc pivoted at its centre has a spring ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform vertical rod of mass m and length l pivoted at point O ...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal and opposite forces are allplied tangentially to a uniform d...
Text Solution
|
- A dog of mass m is walking on a pivoted disc of radius R and mass M in...
Text Solution
|