Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
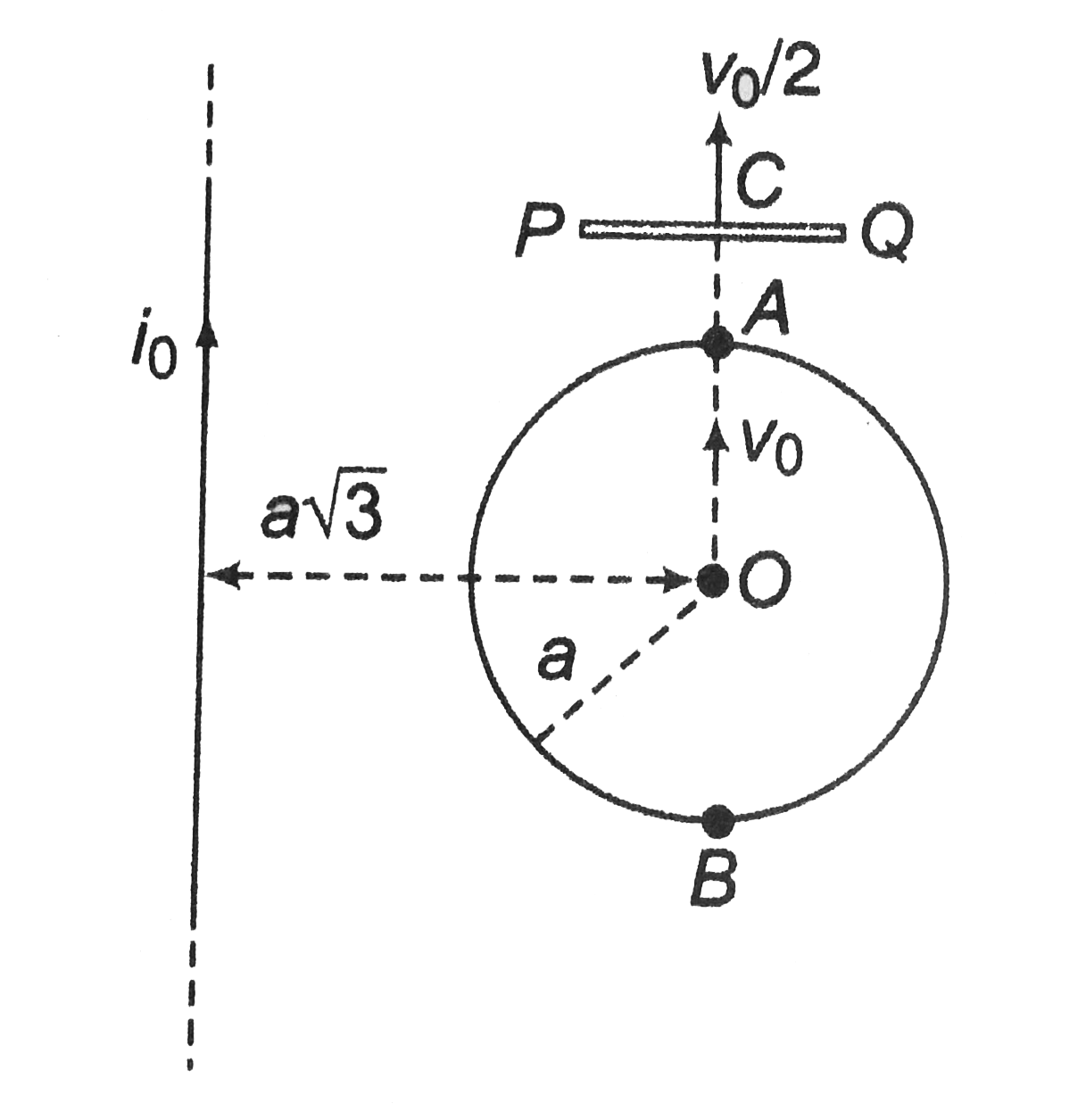
- A conducting circular loop of radius a and resistance per unit length ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting circular loop of radius a and resistance per unit length ...
Text Solution
|
- The radius of the circular conducting loop shown in is R. magnetic fie...
Text Solution
|
- A current carrying solenoid is approaching a conducting loop as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- A circular conducting loop of radius r(0) and having resistance per un...
Text Solution
|
- An electron moves along the line AB with constant velocity V which lie...
Text Solution
|
- An electron moves along the line AB with constant velocity V which lie...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of negligible dimensions carrying a charge q falls into a conduc...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting wire of 2m length is used to form a circular loop. If it ...
Text Solution
|