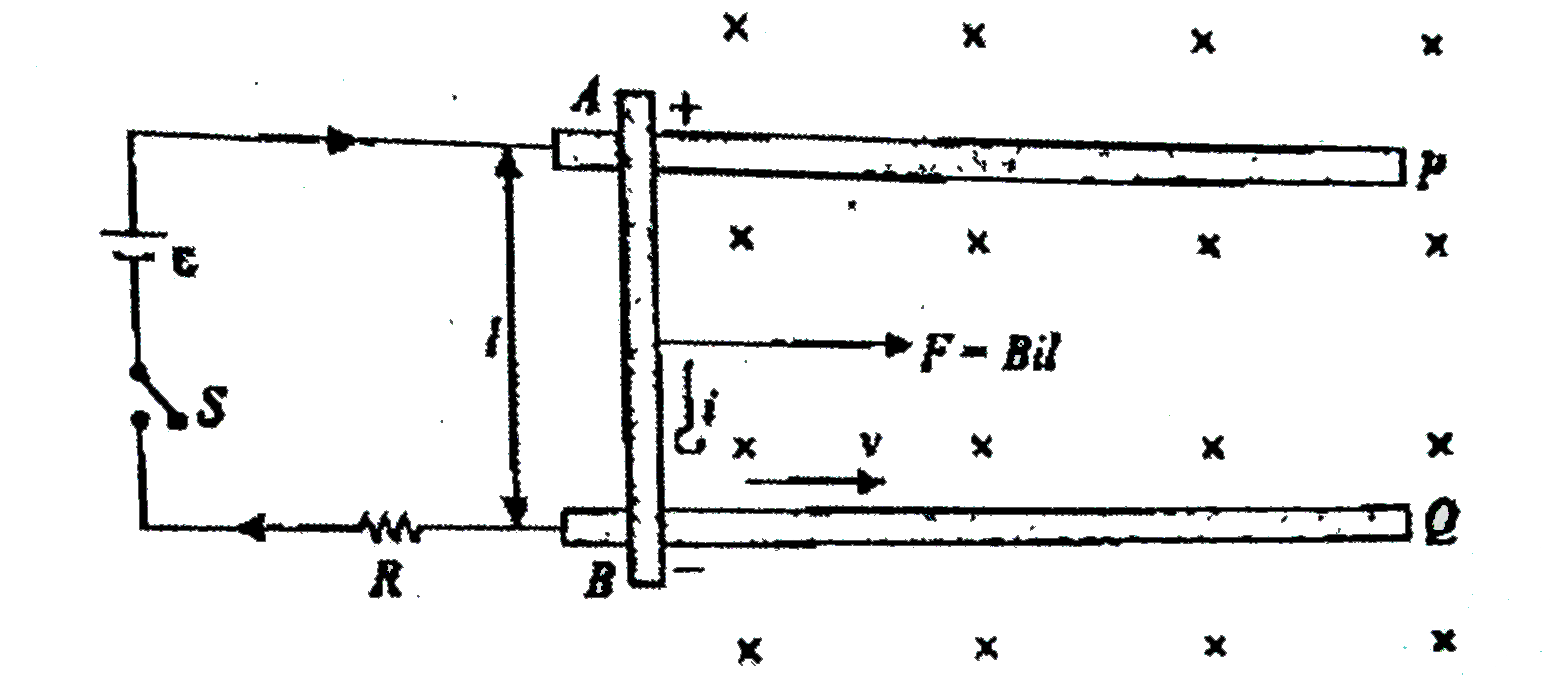Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A uniform rod AB of mass m and length l is placed over two smooth con...
Text Solution
|
- Find the moment of inertia of the rod AB about an axis yy as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod AB of mass m and length l is at rest on a smooth horizon...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod PQ of mass m and length l is placed on two long paral...
Text Solution
|
- Two smooth horizontal parallel conducting rails are connected with a c...
Text Solution
|
- Find the gravitational potential energy of system consisting of unifor...
Text Solution
|
- A rod AB of mass m and length l is placed on two smooth rails P and Q ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the gravitational potential energy of a system consisting of a un...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod AB of mass m and length l is placed over two smooth cond...
Text Solution
|