Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOTION IN A PLANE
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|6 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|10 VideosMOTION IN A PLANE
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise EXERCISE-3 (Circular Motion)|7 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE
AAKASH SERIES|Exercise very Short answer type question|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH SERIES-MOTION IN A PLANE-QUESTION FOR DESCRIPTIVE ANSWER
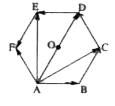
- ABCDEF is a regular hexagon with point O as centre. Find the value of ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected over a triangle from one end of a horizontal...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected at an angle a with horizontal from the foot o...
Text Solution
|
- A stone is projected from the pont of a ground in such a direction...
Text Solution
|
- A stone must be projected horizontally from a point P, which is h ...
Text Solution
|
- A gun is mounted on a gun carriage movable on a smooth plane the gun...
Text Solution
|
- A regular hexagon of side a stand in a vertical plane with one side...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile is given an initial velocity of (hat(i) + 2hat(j)) ms^(-...
Text Solution
|