Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS-II|11 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SELF ASSESSMENT TEST (SECTION A) (MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)|5 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|41 VideosMODEL TEST PAPER 3 (UNSOLVED)
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise SECTION A|3 VideosNUCLEI
U-LIKE SERIES|Exercise Self Assessment Test|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
U-LIKE SERIES-MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM -LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS-I
- Write the expression for the force vecF acting on a charged particle o...
Text Solution
|
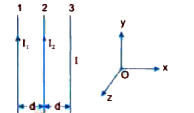
- Two long straight parallel current conductors are kept at a distance d...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangle loop of size l xx b carrying a steady current I is placed ...
Text Solution
|
- Two small identical circular loops, marked (1) and (2), carrying equal...
Text Solution
|
- A circular coil of 200 turns and radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform m...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular loop of wire of size 4 cm xx 10 cm carries a steady curr...
Text Solution
|
- A wire AB is carrying current of 12 A and is lying on the table. Anoth...
Text Solution
|
- A circular coil, having 100 turns of wire of radius (nearly) 20 cm eac...
Text Solution
|
- State the underlying principle of working of a moving coil galvonomete...
Text Solution
|
- A moving coil galvonometer of resistance RG gives a full scale deflect...
Text Solution
|
- A moving coil galvonometer of resistance RG gives a full scale deflect...
Text Solution
|
- Briefly explain how you will convert a moving coil galvonometer into a...
Text Solution
|
- (a) State the principle of working of a galvonometer. (b) A galvonom...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Define the current sensitivity of a galvonometer . (b) The coil ...
Text Solution
|
- A solenoid, of length 1.0 m, has a radius of 1 cm and has a total of 1...
Text Solution
|
- Three long straight parallel wires are kept as shown in the fig. The w...
Text Solution
|
- An electron moves around the nucleus in a hydrogen atom of radius 0.51...
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer with a coil of resistance 120 ohm shows full scale full...
Text Solution
|
- Derive an expression for the magnetic moment vec(mu) of an electron re...
Text Solution
|
- An electron of mass me, revolves around a nucleus of charge +Ze. Show ...
Text Solution
|